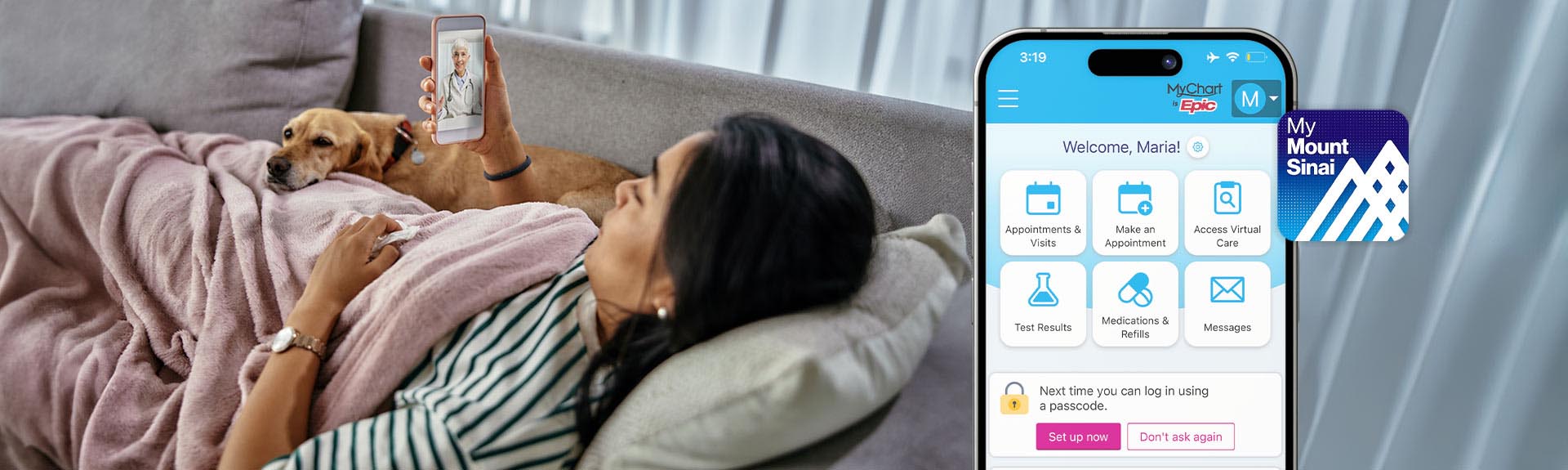
Get More Control Over Your Health Care with MyMountSinai
In our new videos, learn about features of our MyMountSinai app making it easier to book appointments, access virtual care, message your care team, and more

Unsure What to Do When You're Not Feeling Well?
Take our symptoms assessment and view your care options with our new Check Symptoms & Get Care tool
Center for Post-COVID Care at Mount Sinai
Center to provide post-multidisciplinary care and psychosocial resources for patients recovering from COVID-19.
Patient Care and Services
The Mount Sinai Health System offers unparalleled clinical care, backed by advanced research and expertise in all medical disciplines. This newly established system provides patients with the full range of clinical care specialties and treatments, as well as a vast network of facilities. Explore our Service Areas below and discover the Mount Sinai difference.
Breast Health
- Dubin Breast Center of the Tisch Cancer Institute
- The Blavatnik Family – Chelsea Medical Center at Mount Sinai
Comprehensive Health Program at Mount Sinai Fuster Heart Hospital
Digestive Diseases/Gastroenterology
Ear, Nose and Throat/Head and Neck Surgery
East Harlem Health Outreach Partnership
Emergency Services
Family Medicine and Community Health
Heart/Cardiology and Cardiovascular Surgery
- Mount Sinai Brooklyn Ambulatory Infusion Center
- The Blavatnik Family – Chelsea Medical Center at Mount Sinai
- The Mount Sinai Therapeutic Infusion Center
- Mount Sinai Queens
- Mount Sinai Tisch Cancer Center and Infusion Center
International Patient Services
Military Family Health Services
Mount Sinai Selikoff Centers for Occupational Health
OBGYN and Reproductive Services
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- The Mount Sinai Hospital
- Mount Sinai West
- Mount Sinai-Union Square
- The Blavatnik Family – Chelsea Medical Center at Mount Sinai
- Mount Sinai Brooklyn
- The Mount Sinai Hospital
- New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai
- Mount Sinai Queens
- Mount Sinai Morningside
- Mount Sinai West
- Mount Sinai Express Care
- Mount Sinai-Union Square Urgent Care
- Mount Sinai-Urgent Care, East 14th Street
- Mount Sinai Urgent Care and Multispecialty Physicians Upper West Side