"Common Cranial Birth Defect: Mount Sinai Researchers Validate Genetic Links"
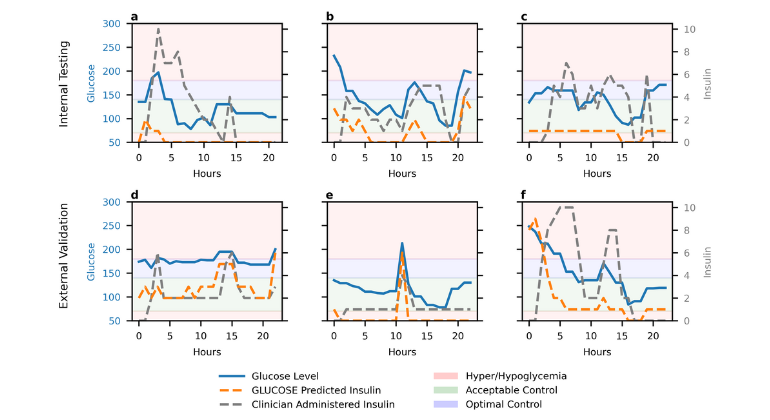
Researchers at Mount Sinai School of Medicine have validated new genetic links for sagittal craniosynostosis, a common birth defect in which the bones that form the sides and top of the skull fuse prematurely. The genome-wide association (GWA) study and replication, published online November 18th in the journal Nature Genetics, provides the first strong evidence of genetic variants contributing to non-syndromic sagittal craniosynostosis. "Genetic markers near the bone morphogenetic protein gene on chromosome 7 and also within the Bardet-Biedel syndrome 9 gene on chromosome 20 were found, and we replicated it with 172 cases and 548 controls," said Ethylin Wang Jabs, MD, PhD, Professor of Genetics and Genomic Sciences, Developmental and Regenerative Biology, and Pediatrics at Mount Sinai School of Medicine. "This association suggests that individuals carrying these genetic markers may have more than a four-fold risk of having sagittal craniosynostosis," added Inga Peter, PhD, Associate Professor of Genetics and Genomic Sciences. Learn more
Mount Sinai Surgeons Perform First Heart-Liver-Kidney Transplants in New York State
May 20, 2025 View All Press Releases
Mount Sinai Study Advances Understanding of Personalized Vaccines for Bladder Cancer
May 12, 2025 View All Press Releases