Edoxaban May Be Effective Treatment for Atrial Fibrillation After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
Mount Sinai study is first to compare this anticoagulant with the standard of care in large randomized clinical trial
The anticoagulant edoxaban may be just as effective as warfarin for preventing heart attack or stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) who undergo transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), according to a large-scale international study led by Mount Sinai.
The ENVISAGE-TAVI AF trial is the largest to investigate an edoxaban-based strategy in this patient population compared with warfarin, which is currently the standard of care. It demonstrates that edoxaban is non-inferior to warfarin. The results, which could lead to an alternative treatment strategy, were announced Saturday, August 28, as a late-breaking clinical trial at the ESC Congress 2021 from the European Society of Cardiology and simultaneously published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“Atrial fibrillation after transcatheter aortic valve replacement is common, especially among older patients, but there has been little research on the optimal treatment strategies, and this has resulted in heterogeneous use of anticoagulants in clinical practice. TAVR patients are typically very elderly and possess numerous comorbidities; therefore they are at high risk for all sorts of adverse events, both ischemic and bleeding. It is important to further understand what treatment is most effective to prevent devastating complications,” says lead investigator George Dangas, MD, PhD, Professor of Medicine (Cardiology) and Director of Cardiovascular Innovation at the Zena and Michael A. Wiener Cardiovascular Institute at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. “Based on these results, the trial met its primary endpoint of non-inferiority and edoxaban may be a plausible alternative to warfarin, albeit with attention to increased bleeding with this agent in this study population.”
Cardiologists prescribe antithrombotic agents—specifically warfarin, a vitamin K antagonist—to prevent thromboembolic complications in patients who have TAVR, a minimally invasive heart procedure to replace the aortic valve. Choosing the optimal antithrombotic regimen remains challenging, especially in patients with an underlying condition like AF—irregular rapid heartbeat that impacts blood flow—that requires the use of anticoagulants. Past studies have shown anywhere between 20-40 percent of TAVR patients have AF and a large proportion of them are frail, so a main challenge in managing their care involves balancing the risks of bleeding and stroke.
Until now, there has been minimal research into the optimal oral anticoagulation therapy in TAVR patients.
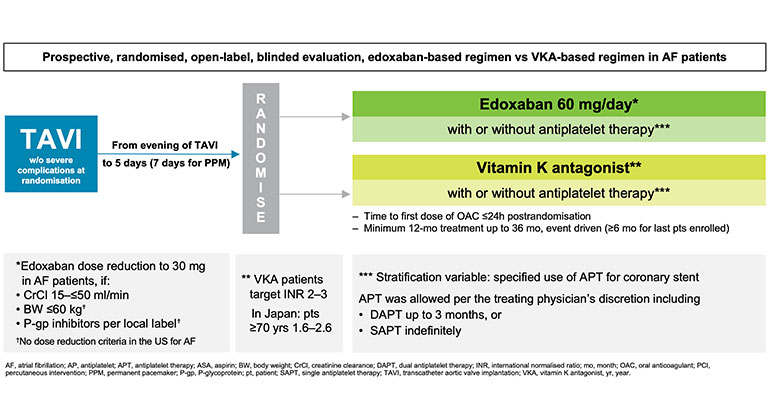
Mount Sinai researchers led an international trial across 173 centers in 14 countries to compare the safety and efficacy of edoxaban versus warfarin in AF patients who need oral anticoagulation. To determine efficacy, they looked at combined adverse clinical events including all-cause death, thromboembolic events, and major bleeding. For safety they looked at serious bleeding events. Investigators randomized 1,426 patients 5 to 12 days after TAVR to either warfarin (with or without antiplatelet therapy) or 60 mg daily oral edoxaban (with or without antiplatelet therapy). They followed up with patients for up to three years following TAVR (average of 18 months). The study findings showed that edoxaban was noninferior to warfarin for efficacy as assessed by a composite set of ischemic and bleeding adverse events. At the same time, edoxaban led to some higher bleeding complications (mainly gastrointestinal) when compared to warfarin (or its analogs as available in each country).
Interestingly, patients who received a lower dose of edoxaban (30 mg instead of 60 mg) due to poor kidney function or low body weight appeared to have similar rates of adverse thromboembolic and bleeding events to those on warfarin.
“The next step would be to establish in large randomized trials the optimal anticoagulant dose according to different bleeding-ischemic risk profiles,” adds Dr. Dangas. “It seems that lowering the edoxaban dosage when indicated and avoiding patients with mandatory antiplatelet therapy because of their elevated bleeding risk is reasonable safety advice from the clinical point of view. We will be conducting a detailed analysis on various types of bleeding in the near future. ENVISAGE-TAVI AF suggests that treatment with edoxaban can be valuable in the management of this high-risk population of AF patients after TAVI.”
ENVISAGE-TAVI AF was sponsored by Daiichi Sankyo Inc. with a scientific collaboration between scientists of Icahn Mount Sinai and Global Specialty Medical Affairs of Daiichi Sankyo.
Figure 1: Study Design

About the Mount Sinai Health System
Mount Sinai Health System is one of the largest academic medical systems in the New York metro area, with 48,000 employees working across seven hospitals, more than 400 outpatient practices, more than 600 research and clinical labs, a school of nursing, and a leading school of medicine and graduate education. Mount Sinai advances health for all people, everywhere, by taking on the most complex health care challenges of our time—discovering and applying new scientific learning and knowledge; developing safer, more effective treatments; educating the next generation of medical leaders and innovators; and supporting local communities by delivering high-quality care to all who need it.
Through the integration of its hospitals, labs, and schools, Mount Sinai offers comprehensive health care solutions from birth through geriatrics, leveraging innovative approaches such as artificial intelligence and informatics while keeping patients’ medical and emotional needs at the center of all treatment. The Health System includes approximately 9,000 primary and specialty care physicians and 10 free-standing joint-venture centers throughout the five boroughs of New York City, Westchester, Long Island, and Florida. Hospitals within the System are consistently ranked by Newsweek’s® “The World’s Best Smart Hospitals, Best in State Hospitals, World Best Hospitals and Best Specialty Hospitals” and by U.S. News & World Report's® “Best Hospitals” and “Best Children’s Hospitals.” The Mount Sinai Hospital is on the U.S. News & World Report® “Best Hospitals” Honor Roll for 2025-2026.
For more information, visit https://www.mountsinai.org or find Mount Sinai on Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, X, and YouTube.