Mount Sinai Team Offers Additional Data on Efficacy of Blood Thinners for COVID-19 and Insight on Best Potential Regimens
Study is the basis of a new international clinical trial
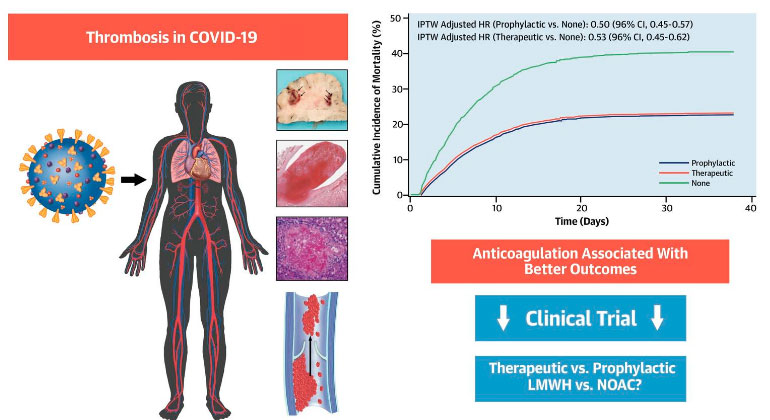
Figure 1: Anticoagulation Associated with Better Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients
Thromboembolic disease is a complication of COVID-19. Prophylactic and therapeutic anticoagulation are associated with better outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. randomized controlled trials evaluating different AC regimens in COVID-19 are needed.
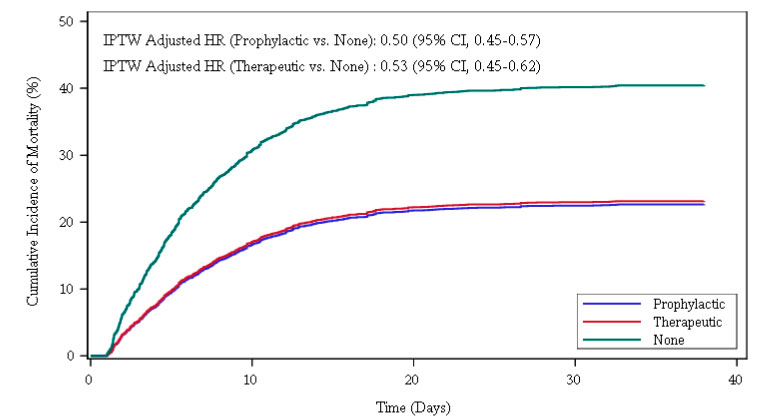
Figure 2: Association of Prophylactic/Therapeutic vs. No Anticoagulation for In-Hospital Mortality
Stabilized weight adjusted cumulative incidence curves for the effect of anticoagulation on in-hospital mortality with discharge as a competing risk.
Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, Mount Sinai researchers were among the first to show that anticoagulation therapy was associated with improved survival among hospitalized COVID-19 patients. But many questions remained—about the size of the potential benefit, and about what dosage of this therapy might be more effective. Now, the research team has suggested some possible answers, in a paper published in the August 26 online issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
In this observational study, the researchers found all regimens of anticoagulants—drugs that prevent blood clotting—were far superior to no anticoagulants in COVID-19 patients. More specifically, patients on both a “therapeutic” or full dose, and those on a “prophylactic” or lower dose, showed about a 50 percent higher chance of survival, and roughly a 30 percent lower chance of intubation, than those not on anticoagulants. The researchers looked at six different anticoagulant regimens, including both oral and intravenous dosing, within both therapeutic and prophylactic groups. They observed that therapeutic and prophylactic subcutaneous low-molecular weight heparin, and therapeutic oral apixaban may lead to better results.
“This work from the Mount Sinai COVID Informatics Center provides additional insight on the role of anticoagulation in the management of patients admitted to the hospital with COVID-19. Although this is an observational study, it helped in the design of a large-scale international clinical trial that we are coordinating. The randomized trial focuses on those three antithrombotic regimens— therapeutic and prophylactic subcutaneous low-molecular weight heparin, and therapeutic oral apixaban,” says senior corresponding author Valentin Fuster, MD, PhD, Director of Mount Sinai Heart and Physician-in-Chief of The Mount Sinai Hospital.
This study is an extension of Mount Sinai research that showed that treatment with anticoagulants was associated with improved outcomes both in and out of the intensive care unit among hospitalized COVID-19 patients. The work was prompted by the discovery that many patients hospitalized with COVID-19 developed high levels of life-threatening blood clots.
The team of investigators evaluated electronic medical records of 4,389 confirmed COVID-19-positive patients admitted to five hospitals in the Mount Sinai Health System in New York City (The Mount Sinai Hospital, Mount Sinai West, Mount Sinai Morningside, Mount Sinai Queens, and Mount Sinai Brooklyn) between March 1 and April 30, 2020. They specifically looked at survival and death rates for patients placed on therapeutic and prophylactic doses of blood thinners (oral antithrombotics, subcutaneous heparin, and intravenous heparin) versus those not placed on blood thinners. The researchers used a hazard score to estimate risk of death, which took relevant risk factors into account before evaluating the effectiveness of anticoagulation, including age, ethnicity, pre-existing conditions, and whether the patient was already on blood thinners. The researchers also took into account and corrected for disease severity, including low oxygen saturation levels and intubation.
Of the patients analyzed, 900 (20.5 percent) received a full-treatment dose of anticoagulants. Another 1,959 patients (44.6 percent) received a lower, prophylactic dose of anticoagulants, and 1,530 (34.5 percent) were not given blood thinners. There was a strong association between blood thinners and reduced likelihood of in-hospital deaths: both therapeutic and prophylactic doses of anticoagulants reduced mortality by roughly 50 percent compared to patients on no blood thinners.
Overall, 467 (10.6 percent) of the patients required intubation and mechanical ventilation during their hospitalization. Those on therapeutic blood thinners had 31 percent fewer intubations than those not on blood thinners, while those on prophylactic blood thinners had 28 percent fewer.
Bleeding rates—a known complication of blood thinners—were surprisingly low overall among all patients (three percent or less), but slightly higher in the therapeutic group compared to the prophylactic and no-blood-thinner groups, the researchers said. Their findings suggest that clinicians should evaluate patients on an individual basis given the benefit-risk tradeoff.
Separately, the researchers looked at autopsy results of 26 COVID-19 patients and found that 11 of them (42 percent) had blood clots—pulmonary, brain, and/or heart—that were never suspected in the clinical setting. These findings suggest that treating patients with anticoagulants may be associated with improved survival.
“This report is much more in-depth than our previous brief report and includes many more patients, longer follow-up, and rigorous methodology. Clearly, anticoagulation is associated with improved outcomes and bleeding rates appear to be low,” says corresponding author Anu Lala, MD, Assistant Professor of Medicine (Cardiology) and Director of Heart Failure Research at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. “As a clinician who has treated COVID-19 patients on the front lines, I recognize the importance of having answers as to what the best treatment for these patients entails, and these results will inform the design of clinical trials to ultimately give concrete information.”
"These observational analyses were done with the highest level of statistical rigor and provide exciting insights into the association of anticoagulation with critical in-hospital outcomes of mortality and intubation," says first author Girish Nadkarni, MD, Co-Founder and Co-Director of the Mount Sinai COVID Informatics Center and Clinical Director of the Hasso Plattner Institute for Digital Health at Mount Sinai. “We are excited that results from this observational study in one of the largest and most diverse hospitalized populations have led to an ongoing trial of type, duration, and doses of anticoagulation. Ultimately we hope this work will lead to improved outcomes and treatment for COVID-19 patients."
“This work highlights the need to better understand the disease from a diagnostic and therapeutic point of view and the importance of conducting properly designed diagnostic and interventional studies,” explains co-author Zahi Fayad, PhD, Co-Founder of the Mount Sinai COVID Informatics Center and Director of Mount Sinai’s BioMedical Engineering and Imaging Institute.
About the Mount Sinai Health System
Mount Sinai Health System is one of the largest academic medical systems in the New York metro area, with 48,000 employees working across seven hospitals, more than 400 outpatient practices, more than 600 research and clinical labs, a school of nursing, and a leading school of medicine and graduate education. Mount Sinai advances health for all people, everywhere, by taking on the most complex health care challenges of our time—discovering and applying new scientific learning and knowledge; developing safer, more effective treatments; educating the next generation of medical leaders and innovators; and supporting local communities by delivering high-quality care to all who need it.
Through the integration of its hospitals, labs, and schools, Mount Sinai offers comprehensive health care solutions from birth through geriatrics, leveraging innovative approaches such as artificial intelligence and informatics while keeping patients’ medical and emotional needs at the center of all treatment. The Health System includes approximately 9,000 primary and specialty care physicians and 10 free-standing joint-venture centers throughout the five boroughs of New York City, Westchester, Long Island, and Florida. Hospitals within the System are consistently ranked by Newsweek’s® “The World’s Best Smart Hospitals, Best in State Hospitals, World Best Hospitals and Best Specialty Hospitals” and by U.S. News & World Report's® “Best Hospitals” and “Best Children’s Hospitals.” The Mount Sinai Hospital is on the U.S. News & World Report® “Best Hospitals” Honor Roll for 2025-2026.
For more information, visit https://www.mountsinai.org or find Mount Sinai on Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, X, and YouTube.


