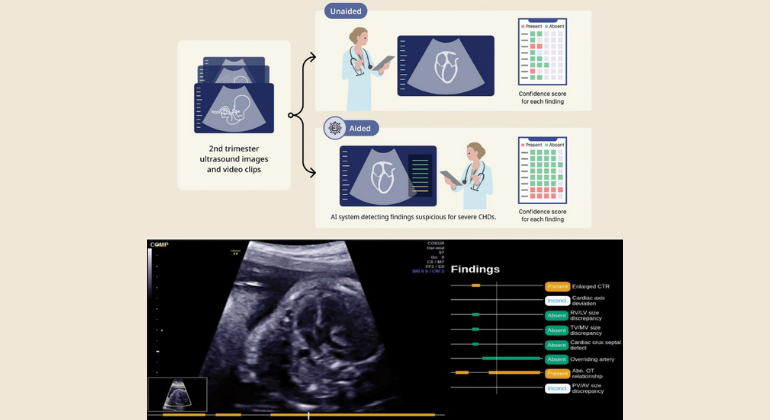
ADHD Drug Works by Stimulating Brain’s Motivation-Reward System
Activity in the regions of the brain associated with motivation and reward correlated with clinical improvements in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms in adults given lisdexamfetamine dimesylate, the results of an imaging study have shown. "What we saw is that Vyvanse (lisdexamfetamine dimesylate) increases activity in the caudate and anterior cingulate, which then seems to show that the medication increases sensitivity to reward," said Stephanie Duhoux, PhD, Postdoctoral Fellow Psychiatry at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, in an interview about her poster presentation at a meeting of the American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology
-Dr. Stephanie Duhoux, Postdoctoral Fellow Psychiatry at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
Mount Sinai Study Finds PTSD May Accelerate Brain Aging in 9/11 Responders
Dec 08, 2025 View All Press Releases
Mount Sinai Showcases Hematology Research at the 67th ASH Annual Meeting
Dec 03, 2025 View All Press Releases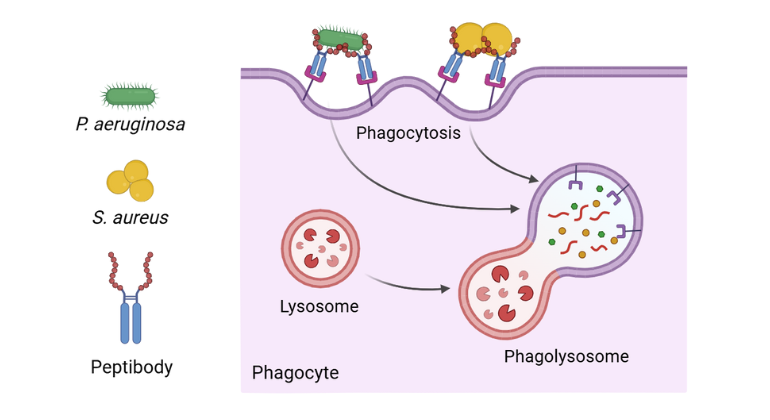
Experimental mRNA Therapy Shows Potential to Combat Antibiotic-Resistant Infections
Nov 26, 2025 View All Press Releases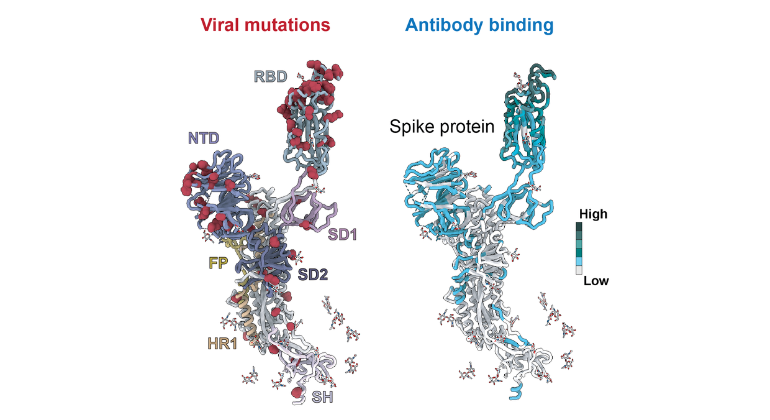
Scientists Uncover How COVID-19 Variants Outsmart the Immune System
Nov 21, 2025 View All Press Releases