Pap test
Papanicolaou test; Pap smear; Cervical cancer screening - Pap test; Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia - Pap; CIN - Pap; Precancerous changes of the cervix - Pap; Cervical cancer - Pap; Squamous intraepithelial lesion - Pap; LSIL - Pap; HSIL - Pap; Low-grade Pap; High-grade Pap; Carcinoma in situ - Pap; CIS - Pap; ASCUS - Pap; Atypical glandular cells - Pap; AGUS - Pap; Atypical squamous cells - Pap; HPV - Pap; Human papilloma virus - Pap cervix - Pap; Colposcopy - Pap; Cervical cytology
The Pap test mainly checks for changes that may turn into cervical cancer. Cells scraped from the opening of the cervix are examined under a microscope. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus (womb) that opens at the top of the vagina.
This test is sometimes called a Pap "smear" or "cervical cytology."
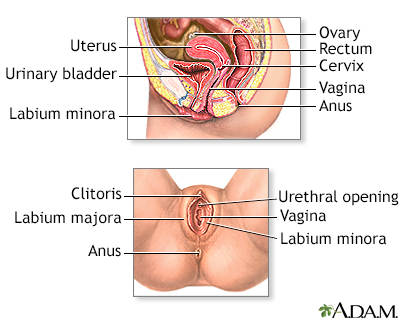
Internal structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the uterus, ovaries, and cervix. External structures include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris.
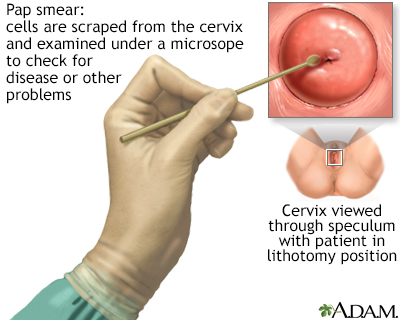
A Pap test is a simple, relatively inexpensive procedure that can easily detect cancerous or precancerous conditions.
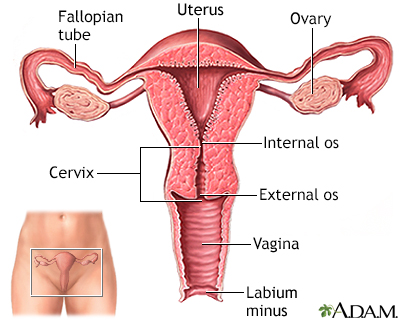
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
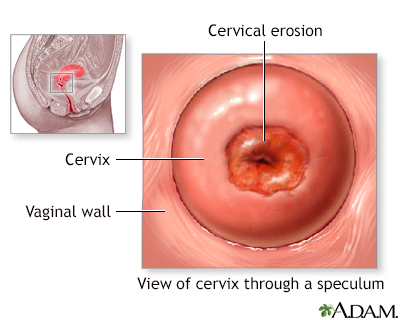
Cervical erosion occurs when the surface of the cervix is replaced with inflamed tissue from the cervical canal. The condition may be caused by trauma, infection or chemicals.
How the Test is Performed
You lie on a table and place your feet in footrests. Your health care provider gently inserts an instrument called a speculum into your vagina to open it slightly. This allows the provider to see your cervix.
Cells are gently collected from your cervix. The sample of cells is sent to a lab for examination.
If you're a woman 21 or over, it's important to begin getting regular pelvic examinations to take charge of your health. An important part of this pelvic exam may include a test, called a Pap smear, to detect the often life-threatening disease, cervical cancer, even before it starts. And here's the key, cervical cells become abnormal years before they turn to cancer. That gives an excellent window of opportunity. So, what is a Pap smear? A Pap smear is a microscopic examination of cells scraped from the opening of the cervix. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus, or womb, that opens at the top of the vagina. The test looks for cervical cancer or abnormal cells. Most cervical cancers can be found, and treated early, or even before they start, if women have routine Pap smears and pelvic examinations. For this test, you will lie on a table and place your feet in stirrups. The doctor will insert an instrument called a speculum into the vagina and open it slightly to see inside the vaginal canal. Cells are gently scraped from the cervix area, and sent to a lab for examination. When a Pap smear shows abnormal changes, you will need further testing. The next step depends on the results of the Pap smear, and on your previous history of Pap smears, and risk factors you may have for cervical cancer. You may need a biopsy using a light and a low-powered microscope, called colposcopy. You may also need a test to check for infection with human papilloma virus, or HPV, which can cause cervical cancer. If you are diagnosed with cervical cancer, the doctor will order more tests to determine how you should be treated, and how far the cancer has spread. This is called staging. Treatment will depend on the stage of the cancer, the size and shape of the tumor, your age and general health, and your desire to have children in the future. Early cervical cancer can be treated with surgery to remove the abnormal tissue, or freeze abnormal cells, or burn abnormal tissue. Treatment for more advanced cervical cancer may include radical hysterectomy, removal of the uterus and much of the surrounding tissue, including lymph nodes and the upper part of the vagina. Radiation may be used to treat cancer that has spread beyond the pelvis, or if cancer returns. The woman may also have chemotherapy to kill the cancer if the cervical cancer's advanced. The Pap smear test is not 100% accurate and cervical cancer may be missed in a small number of cases. Fortunately, cervical cancer develops very slowly in most women and follow-up Pap smears should identify worrisome changes in plenty of time for treatment. Make sure your doctor knows about all the medicines you are taking. Some, including estrogen and progestins, may affect the result of your Pap smear. Pap smears can be a wonderful, life saving tool.
How to Prepare for the Test
Tell your provider if you:
- Have had an abnormal Pap test or a positive human papillomavirus (HPV) test in the past. HPV is a virus that causes genital warts and cervical cancer.
- Might be pregnant.
DO NOT do the following for 24 hours before the test:
- Douche (douching should never be done)
- Have intercourse
- Use tampons
Try not to schedule your Pap test for when you have your period, but if you are having unexpected bleeding, do not cancel your exam. Your provider will determine if the Pap test can still be done.
For your comfort, you may want to empty your bladder just before the test.
How the Test will Feel
A Pap test causes only mild discomfort for most people. The discomfort it causes is usually similar to menstrual cramps. You may also feel some pressure during the exam.
You may bleed a little bit after the test.
Why the Test is Performed
The Pap test looks for changes in cervical cells that may turn into cervical cancer. Most cervical cancers can be avoided if you have screenings according to the recommended schedule.
Experts disagree about when and how often screening tests for cervical cancer should be done, including Pap tests. Some recommend having Pap tests starting at age 21 and then continuing to have them every 3 years. Others recommend waiting until age 25 and using a primary HPV test (one approved by the FDA for this purpose) to screen for cervical cancer. Discuss this with your provider to choose the best approach for you.
If you are age 30 or over you can do any of the following:
- Continue to have a Pap test every 3 years
- Switch to a test for HPV every 5 years
- Have both the Pap and HPV tests every 5 years
You may not need to have a Pap test if you have had a total hysterectomy (uterus and cervix removed) and have had normal Pap tests in the past.
Most people can stop having Pap tests after age 65 if they've had normal tests in the past. Ask your provider when you should stop screening.
Normal Results
A normal result means there are no abnormal cells present. The Pap test is not 100% accurate, and this is why repeat testing is recommended. Because cervical cancer develops very slowly, repeat Pap tests usually find changes in time for treatment before cancer develops.
What Abnormal Results Mean
The most common abnormal Pap test results are:
Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US)
- This test result is considered a mild change.
- These changes may be due to an HPV infection, inflammation, or lack of estrogen as occurs in menopause.
- Repeat Pap testing or HPV testing is recommended. If an HPV test is positive, colposcopy is recommended.
Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL)
- This test result is considered a mild change.
- These changes are often associated with an active HPV infection but may indicate that a precancer or cancer is present.
- Colposcopy is recommended unless an HPV test is negative, in which case repeat testing in one year is often recommended.
Atypical squamous cells, cannot rule out HSIL (ASC-H)
- This test result is considered a relatively severe change.
- These changes may indicate that a precancer or cancer is present.
- Colposcopy is recommended.
High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL)
- This test result is considered a severe change.
- These changes may indicate that a precancer or cancer is present.
- Colposcopy is recommended.
Atypical glandular cells (AGC)
- This test result is considered a severe change.
- These changes may indicate that there is a precancer or cancer of the cells inside the cervix or uterus.
- Colposcopy is recommended and may include a biopsy of the lining of the uterus.
References
Fontham ETH, Wolf AMD, Church TR, et al. Cervical cancer screening for individuals at average risk: 2020 guideline update from the American Cancer Society. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(5):321-346. PMID: 32729638
Newkirk GR. Pap smear and related techniques for cervical cancer screening. In: Fowler GC, ed. Pfenninger and Fowler's Procedures for Primary Care. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 120.
Perkins RB, Guido RS, Castle PE, et al; 2019 ASCCP Risk-Based Management Consensus Guidelines Committee. 2019 ASCCP Risk-Based Management Consensus Guidelines for Abnormal Cervical Cancer Screening Tests and Cancer Precursors. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2020;24(2):102-131. Erratum in: J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2020;24(4):427. PMID: 32243307
Salcedo MP, Phoolcharoen N, Schmeler KM. Intraepithelial neoplasia of the lower genital tract (cervix, vagina, vulva): etiology, screening, diagnosis, management. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 29.
US Preventive Services Task Force website. Cervical cancer: screening.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 1/1/2023
Reviewed by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor Emeritus, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Internal review and update on 02/10/2024 by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
