Spinal cord trauma
Spinal cord injury; Compression of spinal cord; SCI; Cord compression
Spinal cord trauma is damage to the spinal cord. It may result from direct injury to the cord itself or indirectly from disease of the nearby bones, tissues, or blood vessels.
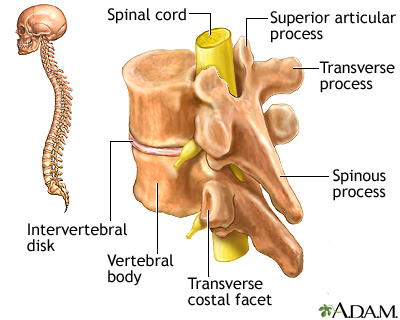
The vertebral column is made up of 26 bones that provide axial support to the trunk. The vertebral column provides protection to the spinal cord, which runs through its central cavity. Between each vertebra is an intervertebral disk, which acts as a shock absorber.
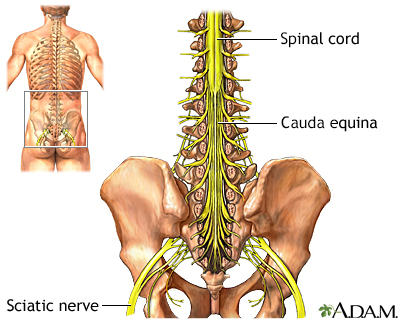
The spinal cord ends in the lumbar area and continues through the vertebral canal as spinal nerves. Because of its resemblance to a horses tail, the collection of these nerves at the end of the spinal cord is called the cauda equina. These nerves send and receive messages to and from the lower limbs and pelvic organs.
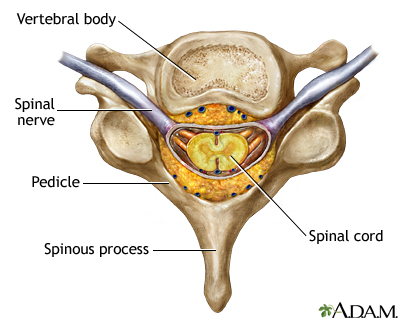
The spinal cord and its peripheral nerves are protected by the vertebral column, a stack of bones which surround and provide support. Between the vertebrae is a fluid-filled disk.
Causes
The spinal cord contains nerve fibers and cells. These nerve fibers carry messages between your brain and body. The spinal cord is located in the spinal canal of your spine in your neck, chest, and back down to the first lumbar vertebra.
Spinal cord injury (SCI) can be caused by any of the following:
- Assault
- Falls
- Gunshot wounds
- Industrial accidents
- Motor vehicle collisions (MVCs)
- Diving
- Sports injuries
A minor injury can damage the spinal cord. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, infection, cancer, or osteoporosis can weaken the spine, which normally protects the spinal cord. Injury can also occur if the spinal canal protecting the spinal cord has become too narrow (spinal stenosis). This occurs due to osteoarthritis of spine joints, usually in older people.
Direct injury or damage to the spinal cord can occur due to:
- Bruises if the bones have been weakened, loosened, or fractured
- Disc herniation (when the disc pushes against the spinal cord)
- Fragments of bone (such as from broken vertebrae, which are the spine bones) in the spinal cord
- Fragments of metal (such as from a motor vehicle collision or gunshot)
- Compression from twisting of the head, neck or back during an accident such as a slip and fall, or intense chiropractic manipulation
- Tight spinal canal (spinal stenosis) that squeezes the spinal cord
- When the spine is out of alignment
Bleeding, fluid buildup, infection, and swelling can occur inside the spinal canal. This can press on the spinal cord and damage it.
Most high impact SCIs, such as from MVCs or sports injuries, are seen in healthy people.
Most low impact SCIs, such as a slip and fall, occur in older individuals with spinal stenosis. Most of these people were not aware they had spinal stenosis.
Risk factors include:
- Participating in risky physical activities
- Riding in or on high-speed vehicles
- Diving into shallow water
Symptoms
Symptoms vary, depending on the location of the injury. SCI causes weakness and loss of feeling at, and below the injury. The severity of the symptoms depends on whether the entire cord is injured (complete) or only partially injured (incomplete). An injury to the upper (cervical) spinal cord will result in weakness or paralysis of the arms and legs. An injury to the middle (thoracic) spinal cord will result in weakness of the legs only.
An injury below the first lumbar vertebra does not cause SCI because the spinal cord turns into a group of nerve roots called the cauda equina. But such an injury may cause cauda equina syndrome, which is an injury to these nerve roots. Many SCIs and cauda equina syndrome cases are emergencies and need surgery right away.
Injuries of the spinal cord at any level may cause:
- Increased muscle tone (spasticity)
- Loss of normal bowel and bladder control (may include constipation, incontinence, bladder spasms)
- Numbness
- Sensory changes
- Pain
- Weakness, paralysis
- Difficulty breathing because of weakness of the abdominal, diaphragm, or intercostal (rib) muscles
CERVICAL (NECK) INJURIES
When SCIs are in the neck area, symptoms can affect the arms, legs, and middle of the body. The symptoms:
- May occur on one or both sides of the body
- Can include severe breathing problems from paralysis of the breathing muscles if the injury is high up in the neck
THORACIC (CHEST LEVEL) INJURIES
When SCIs are at chest level, symptoms can affect the legs. Injuries to the cervical or high thoracic spinal cord may also result in:
- Blood pressure problems (too high and too low)
- Abnormal sweating
- Trouble maintaining normal temperature
LUMBAR OR SACRAL (LOWER BACK) INJURIES
When SCIs are at the lower back level, symptoms can affect one or both legs. Muscles that control the bowels and bladder can also be affected. Spine injuries can damage the spinal cord if they are at the upper portion of the lumbar spine or the lumbar and sacral nerve roots (cauda equina) if they are at the lower lumbar spine.
Exams and Tests
SCI is a medical emergency that needs medical attention right away.
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam, including a brain and nervous system (neurological) exam. This will help identify the exact location of the injury if it is not known.
Some of the reflexes may be abnormal or missing. Once swelling due to the injury goes down, some reflexes may slowly recover.
Tests that may be ordered include:
- CT scan or MRI of the spine
- Myelogram (an x-ray of the spine after injecting dye)
- Spine x-rays
- Electromyography (EMG)
- Nerve conduction studies
- Pulmonary function tests
- Bladder function tests
- Swallowing tests
Treatment
An SCI often needs to be treated right away, except in the elderly with central cord syndrome where early surgery is often of no benefit. The time between the injury and treatment can affect the outcome.
Medicines called corticosteroids are sometimes used in the first few hours after SCI to reduce swelling that may damage the spinal cord.
If spinal cord pressure can be relieved or reduced before the spinal nerves are completely destroyed, paralysis may improve.
Surgery may be needed to:
- Realign the spinal bones (vertebrae)
- Remove fluid, blood, or tissue that presses on the spinal cord (decompression laminectomy)
- Remove bone fragments, disk fragments, or foreign objects
- Fuse broken spinal bones with rods and screws or place spinal braces
Bed rest may be needed to allow the bones of the spine to heal.
Spinal traction may be suggested. This can help keep the spine from moving. The skull may be held in place with tongs. These are metal braces placed in the skull and attached to weights or to a harness on the body (halo vest). You may need to wear the spine braces or a cervical collar for many months.
Your health care team will also tell you what to do for muscle spasms and bowel and bladder dysfunction. They will also teach you how to care for your skin and protect it from pressure sores.
You will probably need physical therapy, occupational therapy, and other rehabilitation programs after the injury has healed. Rehabilitation will help you cope with the disability from your SCI.
You might need blood thinners to prevent blood clots in your legs or medicine to prevent infections such as urinary tract infections.
Support Groups
Seek out organizations for additional information on SCI. They can provide support as you recover.
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well a person does depends on the level and severity of injury. Injuries in the upper (cervical) spine lead to more disability than injuries in the lower (thoracic or lumbar) spine.
Paralysis and loss of sensation of part of the body are common. This includes total paralysis or numbness, and loss of movement and feeling. Death is possible, especially if there is paralysis of the breathing muscles.
A person who recovers some movement or feeling within 1 week usually has a good chance of recovering more function, although this may take 6 months or more. Losses that remain after 6 months are more likely to be permanent.
Routine bowel care often takes 1 hour or more each day. Most people with SCI must perform bladder catheterization regularly.
The person's home will usually need to be modified.
Most people with SCI are in a wheelchair or need assistive devices to get around.
Research in the field of spinal cord injury is ongoing, and promising discoveries are being reported.
Possible Complications
The following are possible complications of SCI:
- Blood pressure changes that can be extreme (autonomic hyperreflexia)
- Increased risk for injury to numb areas of the body
- Increased risk for urinary tract infections
- Long-term kidney disease
- Loss of bladder and bowel control
- Loss of sexual function
- Paralysis of limbs (paraplegia, quadriplegia)
- Paralysis of breathing muscles (quadriplegia)
- Problems due to not being able to move, such as deep vein thrombosis, lung infections, skin breakdown (pressure sores), and muscle stiffness
- Shock
- Depression
People living at home with SCI should do the following to prevent complications:
- Get lung (pulmonary) care each day (if they need it).
- Follow all instructions for bladder care to avoid infections and damage to the kidneys.
- Follow all instructions for routine wound care to avoid pressure sores.
- Keep immunizations up to date.
- Maintain routine health visits with their provider.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have a back or neck injury. Call 911 or the local emergency number if you lose movement or feeling. This is a medical emergency.
Managing SCI begins at the site of an accident or injury. Trained paramedics immobilize the injured spine to prevent further nervous system damage.
Someone who may have a SCI should not be moved unless they are in immediate danger.
Prevention
The following measures may help prevent SCIs:
- Proper safety practices during work and play can prevent many SCIs. Use protective equipment for any activity in which an injury is possible.
- Diving into shallow water is a major cause of spinal cord trauma. Check water depth before diving, and look for rocks or other possible objects in the way.
- Football and sledding can often involve sharp blows or abnormal twisting and bending of the back or neck, which can cause SCI. Before sledding, skiing or snowboarding down a hill, check the area for obstacles. Use the right techniques and equipment when playing football or other contact sports.
- Defensive driving and wearing a seat belt reduce the risk of serious injury if there is a car accident.
- Install and use grab bars in the bathroom, and handrails next to stairs to prevent falls.
- People who have poor balance may need to use a walker or cane.
- Highway speed limits should be observed. Do not drink and drive.
References
Cain C, Diaz JJ. Spinal cord injury. In: Vincent J-L, Moore FA, Bellomo R, Marini JJ, eds. Textbook of Critical Care. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 51.
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke website. Spinal cord injury.
Nori S, Watanabe K, Takeda K, et al. Influence of the timing of surgery for cervical spinal cord injury without bone injury in the elderly: A retrospective multicenter study. J Orthop Sci. 2024;29(2):480-485. PMID: 36720671
Sherman AL, Dalal KL. Spinal cord injury rehabilitation. In: Garfin SR, Eismont FJ, Bell GR, Fischgrund JS, Bono CM, eds. Rothman-Simeone and Herkowitz's The Spine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 82.
Yokota K, Wang S, Singh JM, Fehlings MG. Medical management of spinal cord injury. In: Winn HR, ed. Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 336.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 5/10/2024
Reviewed by: Luc Jasmin, MD, Ph.D., FRCS (C), FACS, Department of Neuroscience, Guam Regional Medical City, Guam; Department of Surgery, Johnson City Medical Center, TN; Department of Maxillofacial Surgery at UCSF, San Francisco, CA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
