Tracheostomy
A tracheostomy is a surgical procedure in which an opening through the neck is created via an incision into the trachea (windpipe). A small tracheostomy tube is then placed through this opening to provide an airway to assist with breathing. At Mount Sinai, our highly skilled physicians have decades of experience with this placement and explore all options of removing it with the assistance of speech language therapy.
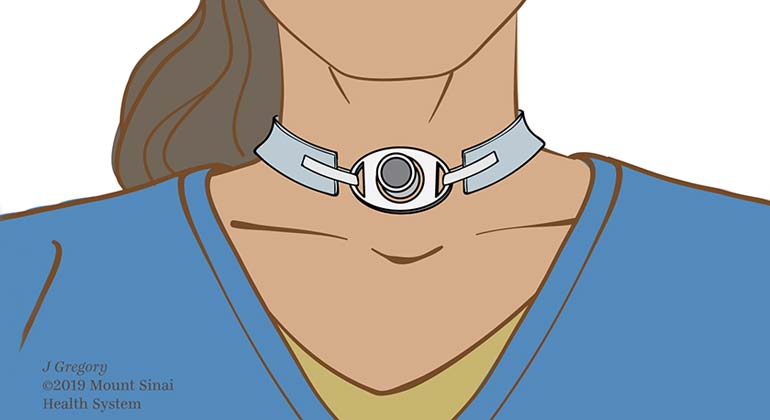
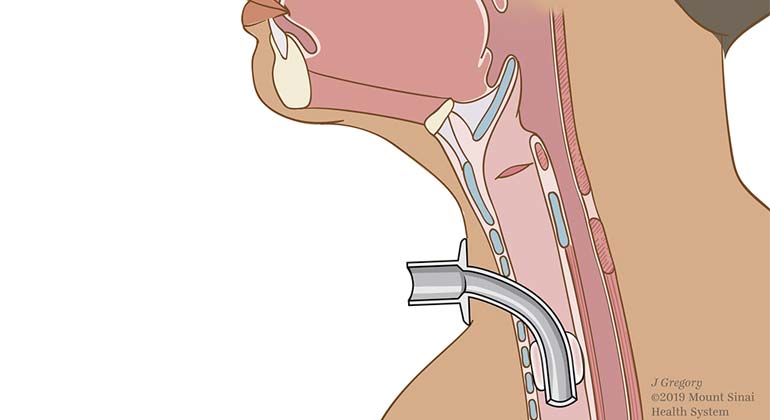
When Tracheostomy is Performed
A tracheostomy may be performed if you or a loved one has or encounters:
- An object blocking the airway
- An inability to breathe independently
- An inherited abnormality of the larynx (voice box) or trachea
- Cancer affecting the neck and airway
- Paralysis of the larynx muscles affecting swallowing
- Severe mouth or neck injuries
- Larynx surgery that prevents normal breathing and swallowing
It may require a few days to adjust to breathing through a tracheostomy tube. And while it may take time to learn how to communicate with others, most patients return to their normal lifestyle.
Tracheostomy Care
The Mount Sinai Health System wants to assist you in understanding the care, equipment, issues and maintenance involved with a tracheostomy. The information herein will serve as a guide. The nurses, doctors, and therapists at Mount Sinai can help you better understand the information and skills that are described.
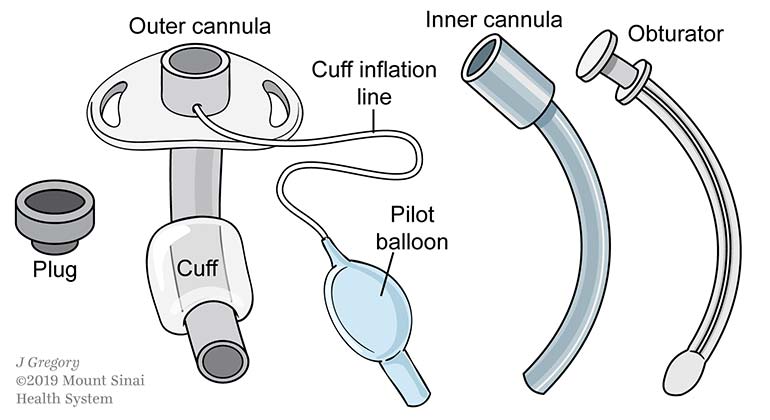
Components of a Tracheostomy
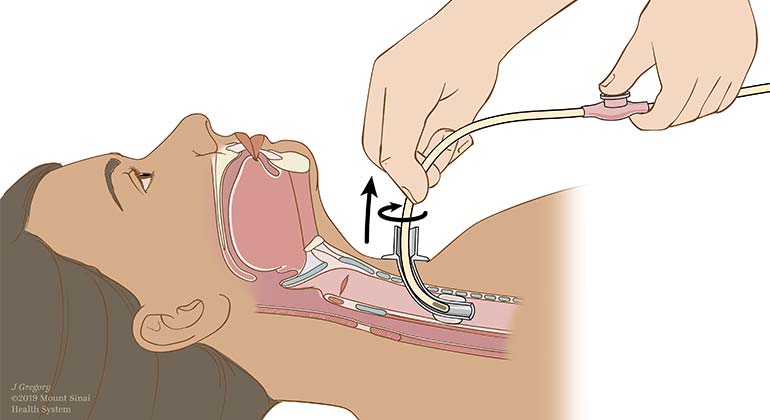
Suctioning a Tracheostomy
- Helpful Videos:
When to Call Your Doctor
If you experience any of the following, contact your Mount Sinai physician:
- Bleeding from the tracheostomy
- Reddening or swollen skin around the stoma (hole) site
- More mucous than usual, or if the mucous becomes yellow, green, or brown
- Foul-smelling mucous
- Fever of 101F or higher