Schirmer test
Tear test; Tearing test; Dry eye test; Basal secretion test; Sjögren - Schirmer; Schirmer's test
The Schirmer test determines whether the eye produces enough tears to keep it moist.
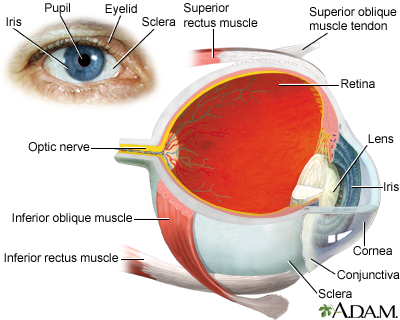
The eye is the organ of sight, a nearly spherical hollow globe filled with fluids (humors). The outer layer or tunic (sclera, or white, and cornea) is fibrous and protective. The middle layer (choroid, ciliary body and the iris) is vascular. The innermost layer (the retina) is nervous or sensory. The fluids in the eye are divided by the lens into the vitreous humor (behind the lens) and the aqueous humor (in front of the lens). The lens itself is flexible and suspended by ligaments which allow it to change shape to focus light on the retina, which is composed of sensory neurons.
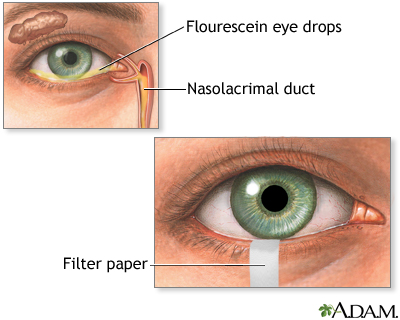
Schirmer's test is used to determine whether the eye produces enough tears to keep it moist. The test is performed by placing filter paper inside the lower lid of the eye. After 5 minutes, the paper is removed and tested for its moisture content.
How the Test is Performed
The health care provider will place the end of a strip of filter paper inside the lower eyelid of each eye. Both eyes are tested at the same time. Before the test, you will be given numbing eye drops to prevent your eyes from tearing due to irritation from the paper strips.
The exact procedure may vary. Most often, the eyes are closed for 5 minutes. Close your eyes gently. Closing the eyes tightly or rubbing the eyes during the test can cause abnormal test results.
After 5 minutes, the provider removes the paper and measures how much of it has become moist.
Sometimes the test is done without numbing drops to test for other types of tear problems.
The phenol red thread test is similar to the Schirmer test, except that red strips of special thread are used instead of paper strips. Numbing drops are not needed. The test takes 15 seconds.
How to Prepare for the Test
You will be asked to remove your glasses or contact lenses before the test.
How the Test will Feel
Some people find that holding the paper against the eye is irritating or mildly uncomfortable. The numbing drops often sting at first.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is used when your provider suspects you have dry eye. Symptoms include dryness of the eyes or excessive watering of the eyes.
Normal Results
More than 10 mm of moisture on the filter paper after 5 minutes is a sign of normal tear production. Both eyes normally release the same amount of tears.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Dry eyes may result from:
- Aging
- Swelling or inflammation of the eyelids (blepharitis)
- Climate changes
- Corneal ulcers and infections
- Eye infections (for example, conjunctivitis)
- Laser vision correction
- Leukemia
- Lymphoma (cancer of the lymph system)
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Previous eyelid or facial surgery
- Sjögren syndrome
- Vitamin A deficiency
Risks
There are no risks with this test.
Considerations
Do not rub the eyes for at least 30 minutes after the test. Leave contact lenses out for at least 2 hours after the test.
Even though the Schirmer test has been available since 1903, several studies show that it does not properly identify a large group of people with dry eyes. Newer and better tests are being developed. One test measures a molecule called lactoferrin. People with low tear production and dry eye have low levels of this molecule.
Another test measures tear osmolarity, or how concentrated the tears are. The higher the osmolarity, the more likely it is that you have dry eye.
References
Akpek EK, Amescua G, Farid Ml; American Academy of Ophthalmology Preferred Practice Pattern Cornea and External Disease Panel, et al. Dry eye syndrome preferred practice pattern. Ophthalmology. 2019;126(1):286-334. PMID: 30366798
Brissette AR, Bohm KJ, Starr CE. Dry eye overview: classification and treatment algorithm. In: Mannis MJ, Holland EJ, eds. Cornea: Fundamentals, Diagnosis and Management. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 31.
Brott NR, Zeppieri M, Ronquillo Y. Schirmer Test. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025.
Chuck RS, Dunn SP, Flaxel CJ; American Academy of Ophthalmology Preferred Practice Pattern Committee, et al. Comprehensive adult medical eye evaluation preferred practice pattern. Ophthalmology. 2021;128(1):P1-P29. PMID: 34933742 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34933742/.
Salmon JF. Dry eye. In: Salmon JF, ed. Kanski's Clinical Ophthalmology. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 5.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 1/20/2025
Reviewed by: Franklin W. Lusby, MD, Ophthalmologist, Lusby Vision Institute, La Jolla, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
