Amniocentesis
Culture - amniotic fluid; Culture - amniotic cells; Alpha-fetoprotein - amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a test that can be done during pregnancy to look for certain problems in the developing baby. These problems include:
- Birth defects
- Genetic problems
- Infection
- Lung development
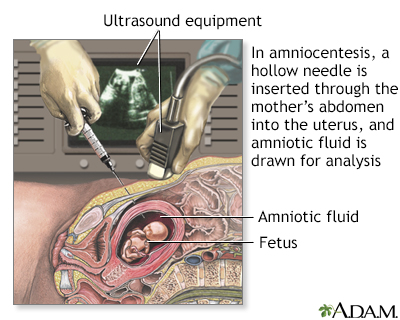
Amniocentesis is used to determine the health of an unborn baby. Amniotic fluid contains cells that are normally shed from the fetus. Samples of these cells are obtained by withdrawing some amniotic fluid. The chromosome analysis of these cells can be performed to determine abnormalities. In addition, the cells may be cultured and analyzed for enzymes, or for other materials that may indicate genetically transmitted diseases. Other studies can be done directly on the amniotic fluid including measurement of alpha-fetoprotein.
In amniocentesis a hollow needle is inserted into the mother's abdomen into the uterus, and amniotic fluid is drawn for analysis.
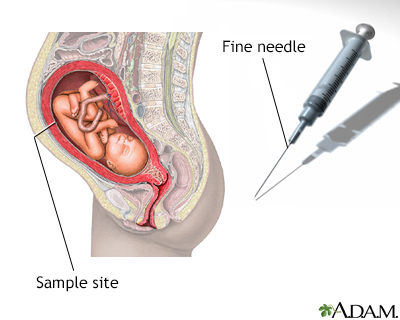
When you are about 15 weeks pregnant, your doctor may offer amniocentesis. Amniocentesis is a test that detects or rules out certain inherited disorders in a fetus. It also assesses lung maturity to see if the fetus can endure an early delivery. You can also find out the baby's gender. Doctors generally offer amniocentesis to women with an increased risk of having a baby with particular disorders. The procedure may be offered to women who will be 35 or older when they deliver, have a close relative with a disorder, or had a previous pregnancy or baby affected by a disorder. It may also be offered if a woman has test results (such as a high or low alpha-fetoprotein count) that may indicate an abnormality. Doctors also offer amniocentesis to women with pregnancy complications, such as Rh-incompatibility, that necessitate early delivery. There are blood tests and ultrasound tests that can be done earlier in the pregnancy which may avoid the need for amniocentesis at times.
How the Test is Performed
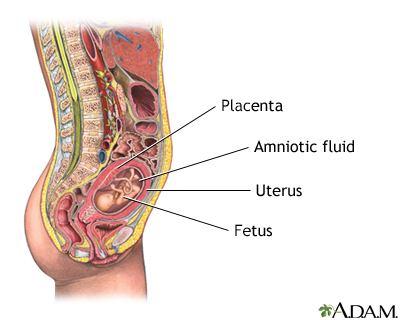
Amniocentesis removes a small amount of fluid from the sac around the baby in the womb (uterus). It is most often done in a doctor's office or medical center. You do not need to stay in the hospital.
You will have a pregnancy ultrasound first. This helps your health care provider see where the baby is in your womb.
Numbing medicine is then rubbed onto part of your belly. Sometimes, the medicine is given through a shot in the skin on the belly area. The skin is cleaned with a disinfecting liquid.
Your provider inserts a long, thin needle through your belly and into your womb. A small amount of fluid (about 4 teaspoons or 20 milliliters) is removed from the sac surrounding the baby. In most cases, the baby is watched by ultrasound during the procedure.
The fluid is sent to a laboratory. Testing may include:
- Genetic studies
- Measurement of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels (a substance produced in the liver of the developing baby)
- Culture for infection
Results of genetic testing usually take about 2 weeks. Other test results come back in 1 to 3 days.
Sometimes amniocentesis is also used later in pregnancy to:
- Diagnose infection
- Check whether the baby's lungs are developed and ready for delivery
- Remove excess fluid from around the baby if there is too much amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios)
How to Prepare for the Test
Your bladder may need to be full for the ultrasound. Check with your provider about this.
Before the test, blood may be taken to find out your blood type and Rh factor. You may get a shot of medicine called Rho(D) Immune Globulin (RhoGAM and other brands) if you are Rh negative.
Why the Test is Performed
Amniocentesis is usually offered to women who are at increased risk of having a child with birth defects. This includes women who:
- Will be 35 or older when they give birth
- Had a screening test that shows there may be a birth defect or other problem
- Have had babies with birth defects in other pregnancies
- Have a family history of genetic disorders
Genetic counseling is recommended before the procedure. This will allow you to:
- Learn about other prenatal tests
- Make an informed decision about options for prenatal diagnosis
This test:
- Is a diagnostic test, not a screening test
- Is most often done between 15 to 20 weeks of your pregnancy, but can be performed at any time between 15 to 40 weeks
Amniocentesis can be used to diagnose many different gene and chromosome problems in the baby, including:
- Anencephaly (when the baby is missing a large portion of the brain)
- Down syndrome
- Rare metabolic disorders that are passed down through families
- Other genetic problems, like trisomy 18 (also known as Edwards syndrome)
- Infections in the amniotic fluid
Normal Results
A normal result means:
- No genetic or chromosome problems found in your baby.
- Bilirubin and alpha-fetoprotein levels appear normal.
- No signs of infection found.
Note: Amniocentesis typically is the most accurate test for genetic conditions and malformation, although rare, a baby may still have genetic or other types of birth defects, even if amniocentesis results are normal.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An abnormal result may mean your baby has:
- A gene or chromosome problem, such as Down syndrome or trisomy 18
- Birth defects that involve the spine or brain, such as spina bifida
Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results. Ask your provider:
- How the condition or defect may be treated during or after your pregnancy
- What special needs your child may have after birth
- What other options you have about maintaining or ending your pregnancy
Risks
Risks are minimal, but may include:
- Infection or injury to the baby
Miscarriage - Leaking of amniotic fluid
- Vaginal bleeding
References
Driscoll DA, Simpson JL. Genetic screening and diagnosis. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 10.
Dugoff L, Wapner RJ. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital disorders. In: Lockwood CJ, Copel JA, Dugoff L, et al, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 30.
Patterson DA, Andazola JJ. Amniocentesis. In: Fowler GC, eds. Pfenninger and Fowler's Procedures for Primary Care. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 144.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 8/23/2023
Reviewed by: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
