Chronic thyroiditis (Hashimoto disease)
Hashimoto thyroiditis; Chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis; Autoimmune thyroiditis; Chronic autoimmune thyroiditis; Lymphadenoid goiter - Hashimoto; Hypothyroidism - Hashimoto; Type 2 polyglandular autoimmune syndrome - Hashimoto; PGA II - Hashimoto; Hashimoto's disease; Hashimoto's thyroiditis
Chronic thyroiditis is caused by a reaction of the immune system against the thyroid gland. It often results in reduced thyroid function (hypothyroidism).
The disorder is also called Hashimoto disease.
The thyroid gland is located in the neck, just above where your collarbones meet in the middle.
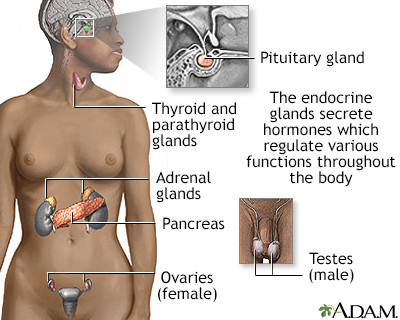
Endocrine glands release hormones (chemical messengers) into the bloodstream to be transported to various organs and tissues throughout the body. For instance, the pancreas secretes insulin, which allows the body to regulate levels of sugar in the blood. The thyroid gets instructions from the pituitary to secrete hormones which determine the rate of metabolism in the body (the more hormone in the bloodstream, the faster the chemical activity; the less hormone, the slower the activity).
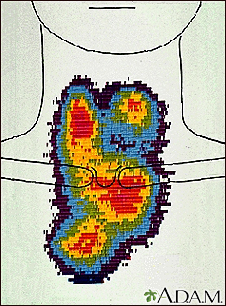
This image shows the enlargement of the thyroid gland and extension down behind the breastbone (retrosternal space). The image, called a scintiscan, was generated using a radioactive isotope.
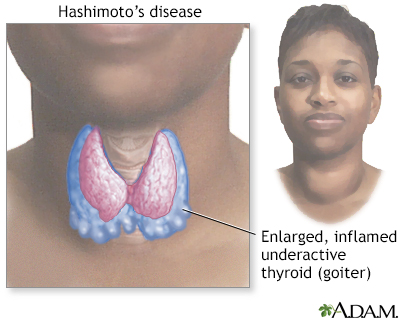
Chronic thyroiditis (Hashimoto's disease) is a slowly developing persistent inflammation of the thyroid which frequently leads to hypothyroidism, a decreased function of the thyroid gland. Middle-aged women are most commonly affected.
The thyroid gland, a part of the endocrine (hormone) system, plays a major role in regulating the body's metabolism.
Causes
Hashimoto disease is a common thyroid gland disorder. It can occur at any age, but is most often seen in middle-aged women. It is caused by a reaction of the immune system against the thyroid gland.
The disease begins slowly. It may take months or even years for the condition to be detected and for thyroid hormone levels to become lower than normal. Hashimoto disease is most common in people with a family history of thyroid disease.
In rare cases, the disease may be related to other hormone problems caused by the immune system. It can occur with poor adrenal function and type 1 diabetes. In these cases, the condition is called type 2 polyglandular autoimmune syndrome (PGA II).
Rarely (usually in children), Hashimoto disease occurs as part of a condition called type 1 polyglandular autoimmune syndrome (PGA I), along with:
- Poor function of the adrenal glands
- Fungal infections of the mouth and nails
- Underactive parathyroid gland
Symptoms
Symptoms of Hashimoto disease may include any of the following:
- Constipation
- Difficulty concentrating or thinking
- Dry skin
- Enlarged neck or presence of a goiter, which may be the only early symptom
- Fatigue
- Hair loss
- Heavy or irregular menstrual periods
- Intolerance to cold
- Mild weight gain
- Mood changes
- Small or shrunken thyroid gland (late in the disease)
Exams and Tests
Laboratory tests to determine thyroid function include:
Imaging studies and fine needle biopsy are generally not needed to diagnose Hashimoto thyroiditis.
This disease may also change the results of the following tests:
- Complete blood count
- Serum prolactin
- Serum sodium
- Total cholesterol
Untreated hypothyroidism can change how your body uses medicines that you may take for other conditions, such as epilepsy. You'll likely need to have regular blood tests to check the levels of the medicines in your body.
Treatment
If you have findings of an underactive thyroid, you may receive thyroid replacement medicine.
Not everyone with thyroiditis or goiter has low levels of thyroid hormone. You may just need regular follow-up by a health care provider.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The disease stays stable for years. If it does slowly progress to thyroid hormone deficiency (hypothyroidism), it can be treated with hormone replacement therapy.
Possible Complications
This condition can occur with other autoimmune disorders. In rare cases, thyroid cancer or thyroid lymphoma may develop.
Severe untreated hypothyroidism can lead to a change in consciousness, coma, and death. This usually occurs if people get an infection, are injured, or take medicines, such as opioids.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you develop symptoms of chronic thyroiditis or hypothyroidism.
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent this disorder. Being aware of risk factors may allow earlier diagnosis and treatment.
References
Brent GA, Weetman AP. Hypothyroidism and thyroiditis. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Golfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 13.
Jonklaas J. Hypothyroidism. In: Robertson RP, ed. DeGroot's Endocrinology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 74.
Pearce EN, Hollenberg AN. Thyroid. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 207.
Wassner AJ, Smith JR. Hypothyroidism. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 581.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 2/28/2024
Reviewed by: Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
