Contact dermatitis
Dermatitis - contact; Allergic dermatitis; Dermatitis - allergic; Irritant contact dermatitis; Skin rash - contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a condition in which the skin becomes red, sore, or inflamed after direct contact with a substance.
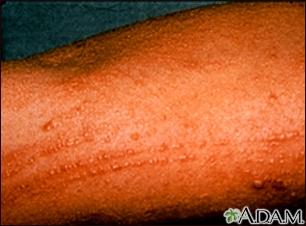
Poison oak rash on the arm. Several plants produce toxins that cause skin reaction. This is the appearance of poison oak dermatitis. Note the typical linear streaks produced either by scratching or brushing against the plant. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
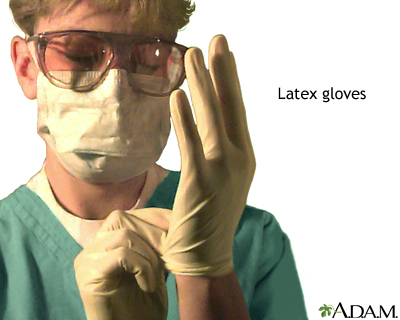
Allergy to latex products may manifest itself in simple dermatitis, or in a more serious whole body reaction, anaphylaxis. The term dermatitis describes an inflammatory response of the skin, caused by contact with allergens or irritants such as the latex in surgical gloves or condoms. Contact with latex may produce an itchy rash, redness, blisters and scaling, or may cause the more severe anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis is a series of symptoms including dropping blood pressure, swelling of the throat and tongue and difficulty breathing.
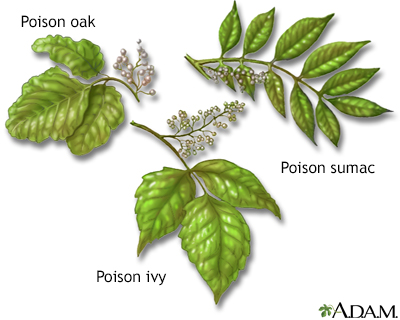
The term dermatitis describes an inflammatory response of the skin, caused by contact with allergens or irritants, exposure to sunlight, or by poor circulation, even stress. An example of contact dermatitis is the reaction of a sensitive person's skin to poison ivy, oak or sumac. Contact with these plants, which contain a chemical called urushiol, produces an itchy rash, redness, blisters and scaling. AVOID SCRATCHING. Scratching the rash may spread the inflammation, lead to infection and even leave scars.
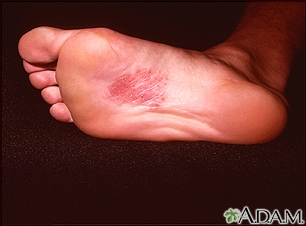
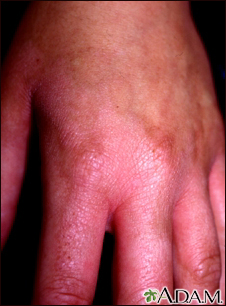
The metal, nickel, can cause inflammation (erythema), rash, and itching. Nickel dermatitis is relatively common, and can be seen on the wrist from the stainless backs of watches, on the earlobes from nickel plated earrings, or elsewhere on the body from snaps. This person was in contact with something made of nickel or containing nickel salts.
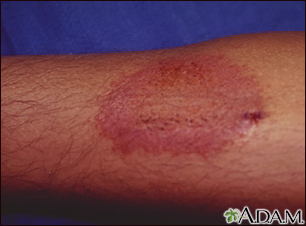
This picture shows a skin inflammation (dermatitis) caused by contact with a material that causes an allergic reaction in this person. Contact dermatitis is a relatively common condition, and can be caused by many substances.
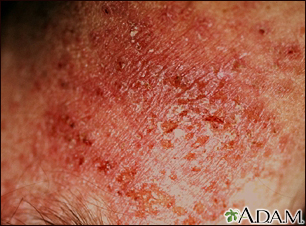
This is an example of an allergic skin reaction (allergic dermatitis) caused by hair dye. The skin on the neck is red (erythematous), thickened (lichenified), scaly, and crusted.
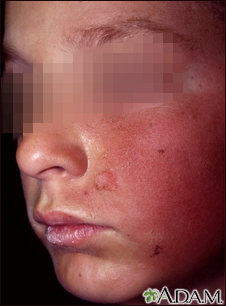
This picture shows a person with a skin inflammation (dermatitis) on the cheek caused by contact with a substance that produced an allergic reaction (allergen). Contact dermatitis causes redness, itching, and small blisters (vesicles).
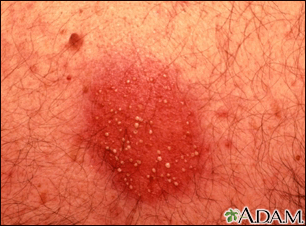
This is a close-up of a dermatitis reaction. It consists of a large, red (erythematous) lesion (plaque) with numerous small pus-filled areas (pustules).
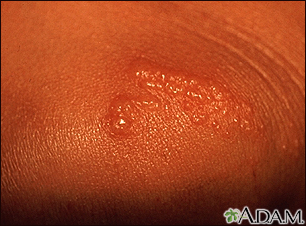
This is a typical early appearance of a poison ivy rash, located on the knee. These early lesions consist of multiple small blisters (vesicles), often in a line where the skin has brushed against the poison ivy plant. The person may then spread the toxin to other areas of the body by scratching.
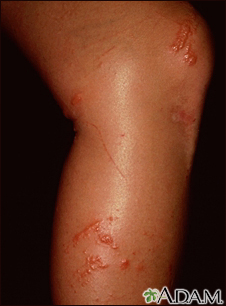
This is a typical early appearance of a poison ivy rash, located on the leg. These early lesions consist of multiple small blisters, often in a line where the skin has brushed against the poison ivy plant. The rash is caused by skin contact with the oily sap (resin) of these plants. The oily resin usually enters the skin rapidly, and is seldom transferred from person to person. The rash is not caused by the fluid from the blisters. Thus, once the person has washed the oil off the skin, the rash is usually not contagious.
This person is sensitive to chemicals used in perfumes, and now develops a rash when the area is exposed to light (photocontact dermatitis). These perfumes include Oil of Bergamot, an oil also found in some citrus fruits and wild plants. It results in streaky redness (erythema) and pigmentary changes.
Causes
There are 2 types of contact dermatitis.
Irritant dermatitis: This is the most common type. It is not caused by an allergy, but rather the skin's reaction to irritating substances or friction. Irritating substances may include acids, alkaline materials such as soaps and detergents, fabric softeners, solvents, or other chemicals. Very irritating chemicals may cause a reaction after just a short period of contact. Milder chemicals can also cause a reaction after repeated contact.
People who have atopic dermatitis are at increased risk of developing irritant contact dermatitis.
Common materials that may irritate your skin include:
- Cement
- Hair dyes
- Long-term exposure to wet diapers
- Pesticides or weed killers
- Rubber gloves
- Shampoos
Allergic contact dermatitis: This form of the condition occurs when your skin comes in contact with a substance that causes you to have an allergic reaction.
Common allergens include:
- Adhesives, including those used for false eyelashes or toupees.
- Antibiotics, such as neomycin rubbed on the surface of the skin.
- Balsam of Peru (used in many personal products and cosmetics, as well as in many foods and drinks).
- Fabrics and clothing, including both materials and dyes.
- Fragrances in perfumes, cosmetics, soaps, and moisturizers.
- Nail polish, hair dyes, and permanent wave solutions.
- Nickel or other metals (found in jewelry, watch straps, metal zips, bra hooks, buttons, pocketknives, lipstick holders, and powder compacts).
- Poison ivy, poison oak, poison sumac, and other plants.
- Rubber or latex gloves or shoes.
- Preservatives commonly used in prescription and over-the-counter topical medicines.
- Formaldehyde, which is used in a broad number of manufactured items.
You will not have an allergic reaction to a substance when you are first exposed to the substance. However, you will form a reaction after future exposures. You may become more sensitive and develop a reaction if you use it regularly. It is possible to tolerate the substance for years or even decades before developing allergy. Once you develop an allergy you will be allergic for life.
The reaction most often occurs 24 to 48 hours after the exposure. The rash may persist for weeks after the exposure stops.
Some products cause a reaction only when the skin is also exposed to sunlight (photosensitivity). These include:
- Shaving lotions
- Sunscreens
- Sulfa ointments
- Some perfumes
- Coal tar products
- Oil from the skin of a lime
A few airborne allergens, such as ragweed, perfumes, vapor from nail lacquer, or insecticide spray, can also cause contact dermatitis.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary, depending on the cause and whether the dermatitis is due to an allergic reaction or an irritant. The same person may also have different symptoms over time.
Allergic reactions may occur suddenly, or develop after months or years of exposure.
Contact dermatitis often occurs on the hands. Hair products, cosmetics, and perfumes can lead to skin reactions on the face, head, and neck. Jewelry can also cause skin problems in the area under it.
Itching is a common symptom. In the case of an allergic dermatitis, itching can be severe.
You may have red, streaky, or patchy rash where the substance touched the skin. The allergic reaction is often delayed so that the rash may not appear until 24 to 48 hours after exposure.
The rash may:
- Have red bumps that may form moist, weeping blisters
- Feel warm and tender
- Ooze, drain, or crust
- Become scaly, raw, or thickened
Dermatitis caused by an irritant may also cause burning or pain as well as itching. Irritant dermatitis often shows as dry, red, and rough skin. Cuts (fissures) may form on the hands. Skin may become inflamed with long-term exposure.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will make the diagnosis based on how the skin looks and by asking questions about substances you may have come in contact with.
Allergy testing with skin patches (called patch testing) may be necessary to determine what is causing the reaction. Patch testing is used for certain people who have long-term or repeated contact dermatitis. It requires at least 3 office visits and must be done by a provider with the skill to interpret the results correctly.
- On the first visit, small patches of possible allergens are applied to the skin. These patches are removed at the second visit 48 hours later to see if a reaction has occurred.
- A third visit, about 2 days later, is done to look for any delayed reaction. For certain allergens such as metals, a final visit may be necessary on the 10th day.
- If you have already tested a material on a small area of your skin and noticed a reaction, you should bring the material with you.
Other tests may be used to rule out other possible causes, including skin lesion biopsy or culture of the skin lesion.
Treatment
Your provider will recommend treatment based on what is causing the problem. In some cases, the best treatment is to do nothing to the area.
Often, treatment includes washing the area with a lot of water to get rid of any traces of the irritant that are still on the skin. You should avoid further exposure to the substance.
Emollients or moisturizers help keep the skin moist, and also help skin repair itself. They protect the skin from becoming inflamed again. They are a key part of preventing and treating irritant contact dermatitis.
Topical corticosteroid medicines are commonly used to treat contact dermatitis.
- Topical means you place it on the skin. You will be prescribed a cream or ointment. Topical corticosteroids may also be called topical steroids or topical cortisones.
- DO NOT use more medicine or use it more often than your provider advises you to use it.
Your provider may also prescribe other creams or ointments, such as tacrolimus or pimecrolimus, to use on the skin.
In severe cases, you may need to take corticosteroid pills. Your provider will start you on a high dose and your dose will be slowly reduced over about 12 days. You may also receive a corticosteroid shot.
Wet dressings and soothing anti-itch (antipruritic) lotions may be recommended to reduce other symptoms.
Topical corticosteroids should be used only for short periods. Long-term use increases the risk of developing more irritant contact dermatitis.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Contact dermatitis clears up without complications in 2 or 3 weeks in most cases. However, it may return if the substance that caused it cannot be determined and avoided.
You may need to change your job or job habits if the disorder is caused by exposure at work. For example, jobs requiring frequent hand washing may be bad choices for people with hand dermatitis.
Sometimes, the allergen causing the allergic contact dermatitis reaction is never identified.
Possible Complications
Bacterial skin infections may occur.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have symptoms of contact dermatitis.
- The skin reaction is severe.
- You do not get better after treatment.
- Signs of infection such as tenderness, redness, warmth, or fever.
References
Dinulos JGH. Contact dermatitis and patch testing. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 4.
James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA, Neuhaus IM. Contact dermatitis and drug eruptions. In: James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA, Neuhaus IM, eds. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 6.
Nixon RL, Allnutt KJ, Diepgen TL. Contact dermatitis. In: Burks AW, Holgate ST, O'Hehir RE, et al, eds. Middleton's Allergy: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 34.
Nixon RL, Mowad CM, Marks JG. Allergic contact dermatitis. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 14.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 7/1/2023
Reviewed by: Ramin Fathi, MD, FAAD, Director, Phoenix Surgical Dermatology Group, Phoenix, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
