Warts
Plane juvenile warts; Periungual warts; Subungual warts; Plantar warts; Verruca; Verrucae planae juveniles; Filiform warts; Verruca vulgaris
Warts are small, usually painless growths on the skin. Most of the time, they are harmless. They are caused by a virus called human papillomavirus (HPV). There are more than 150 types of HPV viruses. Some types of warts are spread through sex.
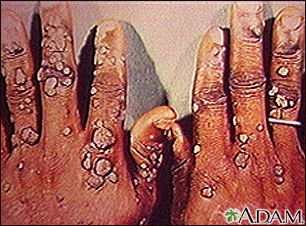
Warts are a very common skin condition. They frequently appear as single lesions or in small groups. This is a photograph of an unusually severe and extensive case of warts. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
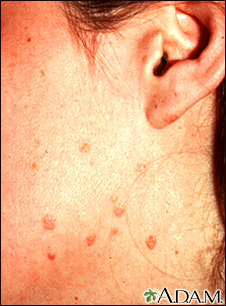
Warts may occur on any area of the body. These are typical looking warts on the face.
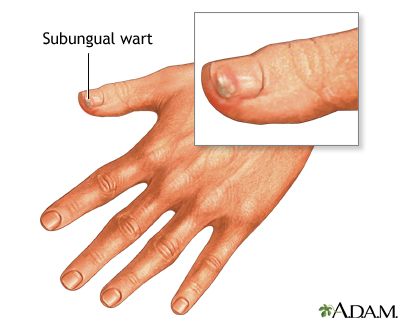
Subungual warts appear under and around the fingernails. These warts are similar to the common wart but are much more difficult to cure than warts found elsewhere on the body.
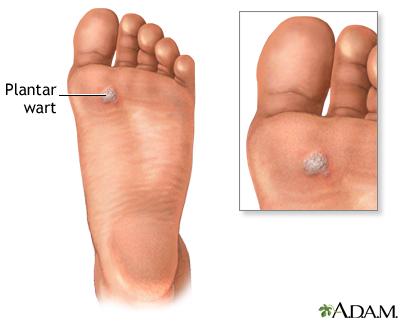
Plantar warts are found on the soles of the feet. Because of their location, they can become extremely painful. Large numbers of plantar warts on the foot may cause difficulty when running and even walking.
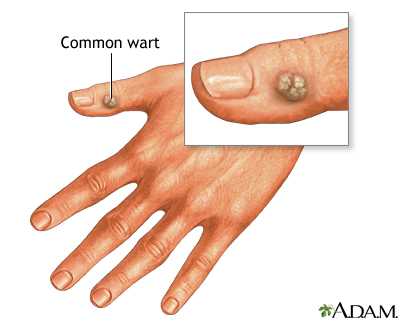
Warts are small, usually painless growths on the skin caused by a virus. The typical wart is a raised round or oval growth on the skin with a rough surface. Common warts tend to cause no discomfort unless they are in areas of repeated friction or pressure. Warts often go away on their own within two years.
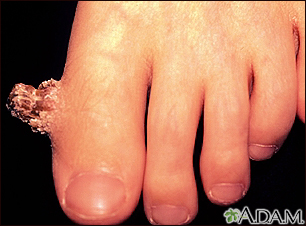
This person has a wart (verruca) that has built up a cutaneous horn which is made up of hard keratin. This does not slough-off like normal skin cells.
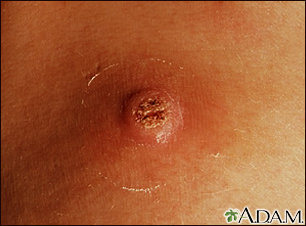
A common wart. A circular bandage.
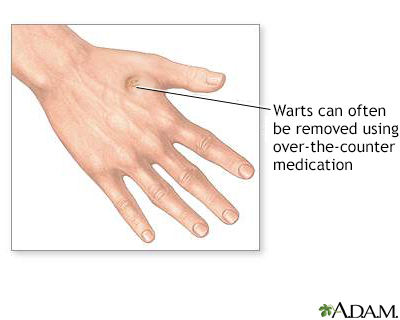
A wart is a benign skin growth caused by a virus. They may occur anywhere on the body but are frequently seen on the hands, feet, and face (areas of frequent contact). Over-the-counter medications are often effective in removal of warts.
Causes
All warts can spread from one part of your body to another. Warts can spread from person to person by contact, especially sexual contact.
If you're a nature lover and find warts on your hand, you don't have to stop picking up frogs or toads. Actually, you have a virus that is pretty harmless, except for your warts being unsightly. Warts are small, usually painless growths on your skin, caused by a type of virus called human papillomavirus (HPV). Even though they're generally harmless, they can be disfiguring and embarrassing, and occasionally they itch or hurt, particularly on your feet. The typical wart is a raised or oval growth on your skin. It has a rough surface. Warts may look light, dark, or black. Most adults are familiar with the look of a typical wart and have little trouble recognizing one. Unusual warts in children, however, may be more difficult for parents to notice. The different types of warts include; Common warts, which usually appear on your hands. Flat warts, which are generally found on your face and forehead. They are most common in children. Genital warts. Plantar warts, found on the soles of your feet. And, Subungual and periungual warts, which appear under and around your fingernails or toenails. Your doctor will generally diagnose your warts simply by their location and appearance. Even so, your doctor may want to cut into a wart to confirm that it is not a corn, callus, or skin cancer. This is called a biopsy. Over-the-counter medications can often remove warts. You'll need to apply them to the wart every day for several weeks. It helps to file the wart down when it's damp (for example, after a bath or shower) before applying these medicines. DO NOT treat warts on your face or genitals yourself. See your doctor instead. You can treat pain and pressure from plantar warts with special cushions you can find at a drug store. If your warts keep coming back, or don't go away, your doctor may use stronger prescription medicines, like podophylin or salicylic acid. Some warts may need to be surgically removed or frozen. Some warts will disappear without treatment, but it may take a couple of years. Treated or not, warts that go away often reappear, and all warts can spread from one part of your own body to another. They can be contagious, but it's uncommon to spread them to another person. Just don't remove a wart yourself by burning, cutting, or tearing at it. Call your doctor, and get the right treatment.
Symptoms
Most warts are raised and have a rough surface. They may be round or oval.
- The spot where the wart is may be lighter or darker than your skin. In rare cases, warts are black.
- Some warts have smooth or flat surfaces.
- Some warts may cause pain.
Different types of warts include:
- Common warts often appear on the hands, but they can grow anywhere.
- Flat warts are generally found on the face and forehead. They are common in children. They are less common in teens, and rare in adults.
- Genital warts usually appear on the genitals, in the pubic area, and in the space between the thighs. They can also appear inside the vagina and anal canal.
- Plantar warts found on the soles of the feet. They can be very painful. Having many of them on your feet may cause problems walking or running.
- Subungual and periungual warts appear under and around the fingernails or toenails.
- Mucosal papillomas occur on mucous membranes, mostly in the mouth or vagina, and are white.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will look at your skin to diagnose warts.
You may have a skin biopsy to confirm the wart is not another type of growth, such as skin cancer.
Treatment
Your provider can treat a wart if you do not like how it looks or if it is painful.
DO NOT attempt to remove a wart yourself by burning, cutting, tearing, picking, or by any other method.
MEDICINES
Over-the-counter medicines are available to remove warts. Ask your provider which treatment is right for you.
DO NOT use over-the-counter wart medicines on your face or genitals. Warts in these areas need to be treated by a provider.
To use wart-removal medicine:
- File the wart with a nail file or emery board when your skin is damp (for example, after a shower or bath). This helps remove dead tissue. Do not use the same emery board on your nails.
- Put the medicine on the wart every day for several weeks or months. Follow the instructions on the label.
- Cover the wart with a bandage.
OTHER TREATMENTS
Special foot cushions can help ease the pain from plantar warts. You can buy these at drugstores without a prescription. Use socks. Wear shoes with plenty of room. Avoid high heels.
Your provider may need to trim away thick skin or calluses that form over warts on your foot or around nails.
Your provider may recommend the following treatments if your warts do not go away:
- Stronger (prescription) medicines
- A blistering solution
- Freezing the wart (cryotherapy) to remove it
- Burning the wart (electrocautery) to remove it
- Laser treatment for difficult-to-remove warts
- Immunotherapy, which gives you a shot of a substance that causes an allergic reaction and helps the wart go away
- Imiquimod, which is applied to warts
Genital warts are treated in a different way than most other warts.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most often, warts are harmless growths that go away on their own within 2 years. Periungual or plantar warts are harder to cure than warts in other places. Warts can come back after treatment, even if they appear to go away. Minor scars can form after warts are removed.
Infection with certain types of HPV can increase cancer risk, most commonly cervical cancer in women. This is most common with genital warts. To decrease the risk for cervical cancer in women, a vaccine is available. Your provider can discuss this with you.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have signs of infection (red streaking, pus, discharge, or fever) or bleeding.
- You have a lot of bleeding from the wart or bleeding that does not stop when you apply light pressure.
- The wart does not respond to self-care, and you want it removed.
- The wart causes pain.
- You have anal or genital warts.
- You have diabetes or a weakened immune system (for example, from HIV) and have developed warts.
- There is any change in the color or appearance of the wart.
Prevention
To prevent warts:
- Avoid direct contact with a wart on another person's skin. Wash your hands carefully after touching a wart.
- Wear socks or shoes to prevent getting plantar warts.
- Use condoms to reduce transmission of genital warts.
- Wash the nail file that you use to file your wart so that you don't spread the virus to other parts of your body.
- Ask your provider about vaccines to prevent some types or strains of viruses that cause genital warts.
- Ask your provider about screening for precancerous lesions, such as by Pap smear.
References
Cadilla A, Alexander KA. Human papillomaviruses. In: Cherry JD, Harrison GJ, Kaplan SL, Steinbach WJ, Hotez PJ, eds. Feigin and Cherry's Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 155.
Dinulos JGH. Warts, herpes simplex, and other viral infections. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 12.
James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA, Neuhaus IM. Viral diseases. In: James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA, Neuhaus IM, eds. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 19.
Kirnbauer R, Lenz P. Human papillomaviruses. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 79.
Long MC. Warts (verrucae). In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, eds. Conn's Current Therapy 2022. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier 2022:1114-1117.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 11/18/2022
Reviewed by: Elika Hoss, MD, Assistant Professor of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
