Abdominal pain
Stomach pain; Pain - abdomen; Belly ache; Abdominal cramps; Bellyache; Stomachache
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.

You know that awful feeling: you're nauseous; your stomach feels like it's tied in a knot, and you don't even want to move. What does your pain mean? Well, let's talk today about abdominal pain. So, what causes abdominal pain? Almost everyone has pain in their belly at one time or another. Most of the time, a serious medical problem is not the cause, and how bad your pain is doesn't always reflect the seriousness of the problem causing your pain. You may feel very bad pain if you are having gas or stomach cramps due to viral gastroenteritis, better known as a stomach virus. And some life-threatening conditions, such as colon cancer or a very early case of appendicitis, may cause only mild pain, or no pain at all. The important thing to know about abdominal pain is when you need immediate medical care. Less serious causes of abdominal pain include constipation, irritable bowel syndrome, food allergies, lactose intolerance, food poisoning, and a stomach virus. Other, more serious, causes include appendicitis, an abdominal aortic aneurysm, a bowel blockage, cancer, and gastroesophageal reflux. Sometimes, you may have abdominal pain from a problem that isn't in your belly, like a heart attack, menstrual cramps, or pneumonia. So, what do you do about abdominal pain? Well, if you have mild abdominal pain, here are some helpful tips; Try sipping water or other clear fluids. Avoid solid food for the first few hours. If you've been vomiting, wait 6 hours and then eat small amounts of mild foods like rice, applesauce, or crackers. If your pain is high in your abdomen and occurs after meals, antacids may help, especially if you are feeling heartburn or indigestion. You should seek medical attention if you have abdominal pain and are being treated for cancer, you can't pass any stool, you're vomiting blood, or you have chest, neck, or shoulder pain. Call your doctor if you have abdominal pain that lasts 1 week or longer, if your pain doesn't improve in 24 to 48 hours, if bloating lasts more than 2 days, or if you have diarrhea for more than 5 days.
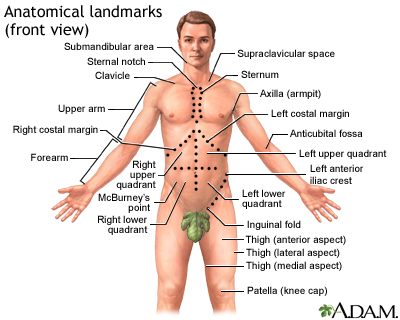
There are three body views (front, back, and side) that can help you to identify a specific body area. The labels show areas of the body which are identified either by anatomical or by common names. For example, the back of the knee is called the “popliteal fossa,” while the “flank” is an area on the side of the body.
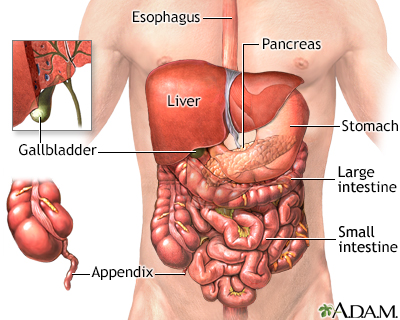
The process of digesting food is accomplished by many organs in the body. Food is pushed by the esophagus into the stomach. The stomach mixes the food and begins the breakdown of proteins. The stomach propels the food then into the small intestine. The small intestine further digests food and begins the absorption of nutrients. Secretions from the pancreas in the small intestine help neutralize the acid in the intestine to provide a proper environment for the enzymes to function. Bile from the gallbladder and liver emulsify fat and enhance the absorption of fatty acids. The large intestine temporarily stores and concentrates the remainder until it is passed out as waste from the body.
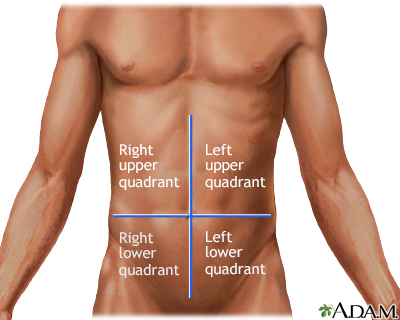
Since the abdominal area contains many different organs it is divided in smaller areas. One division method, uses one median sagittal plane and one transverse plane that passes through the umbilicus at right angles. This method divides the abdomen into four quadrants. Medical personnel can easily refer to these quadrants when describing pain or injury regarding a victim.
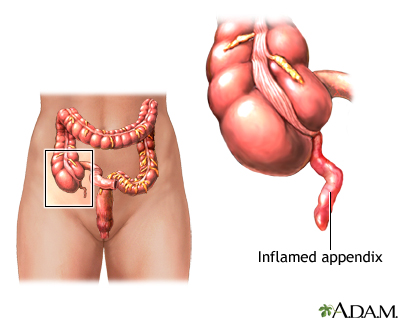
The appendix is a small finger-shaped tube that branches off the first part of the large intestine. The appendix can become inflamed or infected causing pain in the lower right part of the abdomen.
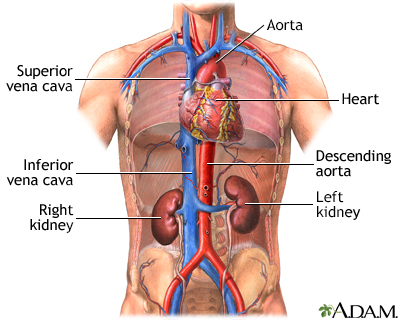
Blood from the aorta reaches the kidneys so it can be filtered and cleaned. Among other functions, the kidneys remove toxins, metabolic waste, and excess ions from the blood which leaves the body in the form of urine.
You know that awful feeling: you're nauseous; your stomach feels like it's tied in a knot, and you don't even want to move. What does your pain mean? Well, let's talk today about abdominal pain. So, what causes abdominal pain? Almost everyone has pain in their belly at one time or another. Most of the time, a serious medical problem is not the cause, and how bad your pain is doesn't always reflect the seriousness of the problem causing your pain. You may feel very bad pain if you are having gas or stomach cramps due to viral gastroenteritis, better known as a stomach virus. And some life-threatening conditions, such as colon cancer or a very early case of appendicitis, may cause only mild pain, or no pain at all. The important thing to know about abdominal pain is when you need immediate medical care. Less serious causes of abdominal pain include constipation, irritable bowel syndrome, food allergies, lactose intolerance, food poisoning, and a stomach virus. Other, more serious, causes include appendicitis, an abdominal aortic aneurysm, a bowel blockage, cancer, and gastroesophageal reflux. Sometimes, you may have abdominal pain from a problem that isn't in your belly, like a heart attack, menstrual cramps, or pneumonia. So, what do you do about abdominal pain? Well, if you have mild abdominal pain, here are some helpful tips; Try sipping water or other clear fluids. Avoid solid food for the first few hours. If you've been vomiting, wait 6 hours and then eat small amounts of mild foods like rice, applesauce, or crackers. If your pain is high in your abdomen and occurs after meals, antacids may help, especially if you are feeling heartburn or indigestion. You should seek medical attention if you have abdominal pain and are being treated for cancer, you can't pass any stool, you're vomiting blood, or you have chest, neck, or shoulder pain. Call your doctor if you have abdominal pain that lasts 1 week or longer, if your pain doesn't improve in 24 to 48 hours, if bloating lasts more than 2 days, or if you have diarrhea for more than 5 days.
Considerations
Almost everyone has pain in the abdomen at some point. Most of the time, it is not serious.
How bad your pain is does not always reflect the seriousness of the condition causing the pain.
For example, you might have very bad abdominal pain if you have gas or stomach cramps due to viral gastroenteritis.
However, fatal conditions, such as colon cancer or early appendicitis, may only cause mild pain or no pain.
Other ways to describe pain in your abdomen include:
- Generalized pain -- This means that you feel it in more than half of your belly. This type of pain is more typical for a stomach virus, indigestion, or gas. If the pain becomes more severe, it may be caused by a blockage of the intestines.
- Localized pain -- This is pain found in only one area of your belly. It is more likely to be a sign of a problem in an organ, such as the appendix, gallbladder, or stomach.
- Cramp-like pain -- This type of pain is not serious most of the time. It is likely to be due to gas and bloating, and is often followed by diarrhea. More worrisome signs include pain that occurs more often, lasts more than 24 hours, or occurs with a fever.
- Colicky pain -- This type of pain comes in waves. It very often starts and ends suddenly, and is often severe. Kidney stones and gallstones are common causes of this type of belly pain.
Causes
Many different conditions can cause abdominal pain. The key is to know when you need to get medical care right away. Sometimes, you may only need to call a health care provider if your symptoms continue.
Less serious causes of abdominal pain include:
- Constipation
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Food allergies or intolerance (such as lactose intolerance)
- Food poisoning
- Stomach flu
Other possible causes include:
- Appendicitis
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm (bulging and weakening of the major artery in the body)
- Bowel blockage or obstruction
- Cancer of the stomach, colon (large bowel), and other organs
- Cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) with or without gallstones
- Decreased blood supply to the intestines (ischemic bowel)
- Diverticulitis (inflammation and infection of the colon)
- Endometriosis
- Heartburn, indigestion, or gastroesophageal reflux (GERD)
- Inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn disease or ulcerative colitis)
- Kidney stones
- Muscle strain
- Pancreatitis (swelling or infection of the pancreas)
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Ruptured ovarian cyst
- Severe menstrual cramps
- Tubal (ectopic) pregnancy
- Ulcers
- Urinary tract infections (UTI)
Home Care
You can try the following home care steps to ease mild abdominal pain:
- Sip water or other clear fluids. You may have sports drinks in small amounts. People with diabetes must check their blood sugar often and adjust their medicines as needed.
- Avoid solid food for the first few hours.
- If you have been vomiting, wait 6 hours, and then eat small amounts of mild foods such as rice, applesauce, or crackers. Avoid dairy products.
- If the pain is high up in your abdomen and occurs after meals, antacids may help, especially if you feel heartburn or indigestion. Avoid citrus, high-fat foods, fried or greasy foods, tomato products, caffeine, alcohol, and carbonated beverages.
- DO NOT take any medicine without talking to your provider.
These additional steps may help prevent some types of abdominal pain:
- Drink plenty of water each day.
- Eat small meals more frequently.
- Exercise regularly.
- Limit foods that produce gas.
- Make sure that your meals are well-balanced and high in fiber. Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Get medical help right away or call your local emergency number (such as 911) if you:
- Are currently being treated for cancer
- Are unable to pass stool, especially if you are also vomiting
- Are vomiting blood or have blood in your stool (especially if bright red, maroon or dark, tarry black)
- Have chest, neck, or shoulder pain
- Have sudden, sharp abdominal pain
- Have pain in, or between, your shoulder blades with nausea
- Have tenderness in your belly, or your belly is rigid and hard to the touch
- Are pregnant or could be pregnant
- Had a recent injury to your abdomen
- Have difficulty breathing
Contact your provider if you have:
- Abdominal discomfort that lasts 1 week or longer
- Abdominal pain that does not improve in 24 to 48 hours, or becomes more severe and frequent and occurs with nausea and vomiting
- Bloating that persists for more than 2 days
- Burning sensation when you urinate or frequent urination
- Diarrhea for more than 5 days
- Fever, over 100°F (37.7°C) for adults or 100.4°F (38°C) for children, with pain
- Prolonged poor appetite
- Prolonged vaginal bleeding
- Unexplained weight loss
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms and medical history. Your specific symptoms, the location of pain and when it occurs will help your provider detect the cause.
LOCATION OF YOUR PAIN
- Where do you feel the pain?
- Is it all over or in one spot?
- Does the pain move into your back, groin, or down your legs?
TYPE AND INTENSITY OF YOUR PAIN
- Is the pain severe, sharp, or cramping?
- Do you have it all the time, or does it come and go?
- Does the pain wake you up at night?
HISTORY OF YOUR PAIN
- Have you had similar pain in the past? How long has each episode lasted?
- When does the pain occur? For example, after meals or during menstruation?
- What makes the pain worse? For example, eating, stress, or lying down?
- What makes the pain better? For example, drinking milk, having a bowel movement, or taking an antacid?
- What medicines are you taking?
OTHER MEDICAL HISTORY
- Have you had a recent injury?
- Are you pregnant?
- What other symptoms do you have?
Tests that may be done include:
- Barium enema
- Blood, urine, and stool tests
- CT scan
- Colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy (tube through the rectum into the colon)
- ECG (electrocardiogram) or heart tracing
- Ultrasound of the abdomen
- Upper endoscopy (tube through the mouth into the esophagus, stomach and upper small intestine)
- Upper GI (gastrointestinal) and small bowel series
- X-rays of the abdomen
References
McQuaid KR. Approach to the patient with gastrointestinal disease. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 123.
Landmann A, Bonds M, Postier R. Acute abdomen. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 46.
Smith KA. Abdominal pain. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 24.
Weber F. Gastrointestinal and hepatic manifestations of systemic diseases. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 37.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 2/7/2022
Reviewed by: Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
