Arterial embolism
Arterial embolism refers to a clot (embolus) that has come from another part of the body and causes a sudden interruption of blood flow to an organ or body part.
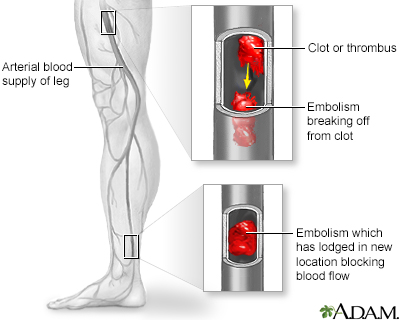
An embolism is a clot that travels from the site where it formed to another location in the body. The embolism can lodge in an artery at the new location and block the flow of blood there. The blockage deprives the tissues in that location of its normal blood flow and oxygen. This can result in damage, destruction, or even death of the tissues (necrosis) in that organ. Arterial embolism requires prompt treatment, usually with hospitalization.
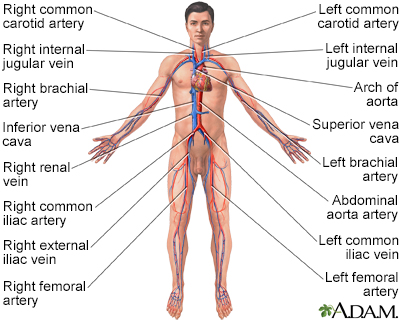
Blood used by the body is brought back to the heart and lungs by the veins of the body. Once the blood has gathered more oxygen from the lungs, it is pumped back out to the body through the arteries.
Causes
An "embolus" is a blood clot or a piece of plaque that acts like a clot. The word "emboli" means there is more than one clot or piece of plaque. When the clot travels from the site where it formed to another location in the body, it is called an embolism.
An arterial embolism may be caused by one or more clots. The clots can get stuck in an artery and block blood flow. The blockage starves tissues of blood and oxygen. This can result in damage or tissue death (necrosis).
Arterial emboli often occur in the legs and feet. Emboli that occur in the brain cause a stroke. Ones that occur in the heart cause a heart attack. Less common sites include the kidneys, intestines, and eyes.
Risk factors for arterial embolism include:
- Abnormal heart rhythms such as atrial fibrillation
- Injury or damage to an artery wall
- Conditions that increase blood clotting
Another condition that poses a high risk for embolization (especially to the brain) is mitral stenosis. Endocarditis (infection of the inside of the heart) can also cause arterial emboli.
A common source for an embolus is from areas of hardening (atherosclerosis causing plaque) in the aorta and other large blood vessels. These clots can break loose and flow down to the legs and feet.
Paradoxical embolization can take place when a clot in a vein enters the right side of the heart and passes through a hole into the left side of the heart. The clot can then move to an artery and block blood flow to the brain (stroke) or other organs.
If a clot travels and lodges in the arteries supplying blood flow to the lungs, it is called a pulmonary embolus.
Symptoms
You may not have any symptoms.
Symptoms may begin quickly or slowly depending on the size of the embolus and how much it blocks the blood flow.
Symptoms of an arterial embolism in the arms or legs may include:
- Cold arm or leg
- Decreased or no pulse in an arm or leg
- Lack of movement in the arm or leg
- Pain in the affected area
- Numbness and tingling in the arm or leg
- Pale color of the arm or leg (pallor)
- Weakness of an arm or leg
Later symptoms:
- Blisters of the skin fed by the affected artery
- Shedding (sloughing) of skin
- Skin erosion (ulcer)
- Tissue death (necrosis; skin is dark and damaged)
Symptoms of a clot in an organ vary with the organ involved but may include:
- Pain in the part of the body that is involved
- Temporarily decreased organ function
Exams and Tests
The health care provider may find decreased or no pulse, and decreased or no blood pressure in the arm or leg. There may be signs of tissue death or gangrene.
Tests to diagnose arterial embolism or reveal the source of emboli may include:
- Angiography of the affected extremity or organ
- Doppler ultrasound exam of an extremity
- Duplex Doppler ultrasound exam of extremity
- Duplex Doppler ultrasound exam of arteries to the brain
- Echocardiogram
- MRI of the arm or leg
- Myocardial contrast echocardiography (MCE)
- Plethysmography
- Transcranial Doppler exam of arteries to the brain
- Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE)
This disease may also affect the results of the following tests:
- D-dimer
- Factor VIII assay
- Isotope study of the affected organ
- Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) activity
- Platelet aggregation test
- Tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) levels
Treatment
Arterial embolism requires prompt treatment at a hospital. The goals of treatment are to control symptoms and to improve the interrupted blood flow to the affected area of the body. The cause of the clot, if found, should be treated to prevent further problems.
Medicines include:
- Anticoagulants (such as warfarin or heparin or one of the newer blood thinners such as apixaban, rivaroxaban, edoxaban, or dabigatran) can prevent new clots from forming
- Antiplatelet medicines (such as aspirin or clopidogrel) can prevent new clots from forming
- Painkillers given through a vein (by IV)
- Thrombolytics (such as streptokinase) can dissolve clots
Some people need surgery. Procedures include:
- Bypass of the artery (arterial bypass) to create a second source of blood supply
- Clot removal through a balloon catheter placed into the affected artery or through open surgery on the artery (embolectomy)
- Opening of the artery with a balloon catheter (angioplasty) with or without a stent
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well a person does depends on the location of the clot and how much the clot has blocked blood flow and for how long the blockage has been present. Arterial embolism can be very serious if not treated promptly.
The affected area can be permanently damaged. Amputation is needed in up to 1 in 4 cases.
Arterial emboli can come back even after successful treatment.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Acute MI
- Infection in the affected tissue
- Septic shock
- Stroke (CVA)
- Temporary or permanent decrease or loss of other organ functions
- Temporary or permanent kidney failure
- Tissue death (necrosis) and gangrene
- Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Go to the emergency room or call 911 or the local emergency number if you have symptoms of arterial embolism.
Prevention
Prevention begins with finding possible sources of a blood clot. Your provider may prescribe blood thinners (such as warfarin or heparin) to prevent clots from forming. Antiplatelet drugs may also be needed.
You have a higher risk atherosclerosis and clots if you:
- Smoke
- Do little exercise
- Have high blood pressure
- Have abnormal cholesterol levels
- Have diabetes
- Are overweight
- Are stressed
References
Aufderheide TP. Peripheral arteriovascular disease. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 73.
Gerhard-Herman MD, Gornik HL, Barrett C, et al. 2016 AHA/ACC guideline on the management of patients with lower extremity peripheral artery disease: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;69(11):1465-1508. PMID: 27851991
Goldman L. Approach to the patient with possible cardiovascular disease. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 45.
Kabrhel C. Pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 74.
Zettervall SL, Schemerhorm ML. Acute mesenteric arterial disease: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical evaluation, and management. In: Sidawy AN, Perler BA, eds. Rutherford's Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 133.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 5/8/2022
Reviewed by: Michael A. Chen, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Harborview Medical Center, University of Washington Medical School, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
